Introduction:
In the expansive universe of digital design, Adobe Illustrator stands tall as a versatile platform that empowers creators to bring their ideas to life with precision and creativity. Among its suite of features, the perspective grid tool emerges as a powerful instrument, offering users the ability to create immersive, three-dimensional scenes with ease. Whether you’re an architect, an illustrator, a graphic designer, or an enthusiast, mastering the perspective grid tool in Adobe Illustrator is essential for crafting dynamic and visually compelling compositions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey to explore the techniques and tools needed to harness the full potential of the perspective grid tool, enabling you to create stunning artworks that captivate and immerse viewers in rich, lifelike environments.
Chapter 1: Introducing the Perspective Grid Tool
At its core, the perspective grid tool in Adobe Illustrator is a transformative feature that allows users to create and manipulate realistic perspective grids within their artwork. By defining one, two, or three-point perspective grids, users can establish a spatial framework that simulates depth and dimension, providing a foundation for creating dynamic and immersive scenes. With intuitive controls and customizable settings, the perspective grid tool offers a seamless experience for generating perspective grids that accurately reflect real-world spatial relationships, empowering users to craft intricate and lifelike compositions with ease.
Chapter 2: Understanding Perspective Grid Options
Before delving into the creation process, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the various options and settings available for the perspective grid tool in Adobe Illustrator. The perspective grid tool panel provides a range of options for customizing the appearance and behavior of the perspective grid, such as grid plane selection, grid line visibility, and grid snapping. Experiment with adjusting settings such as grid plane orientation to define the spatial perspective of your grid, or grid line visibility to control the visibility of grid lines within your artwork. Additionally, explore the perspective grid preferences in the Adobe Illustrator settings to customize default settings such as grid color and opacity.
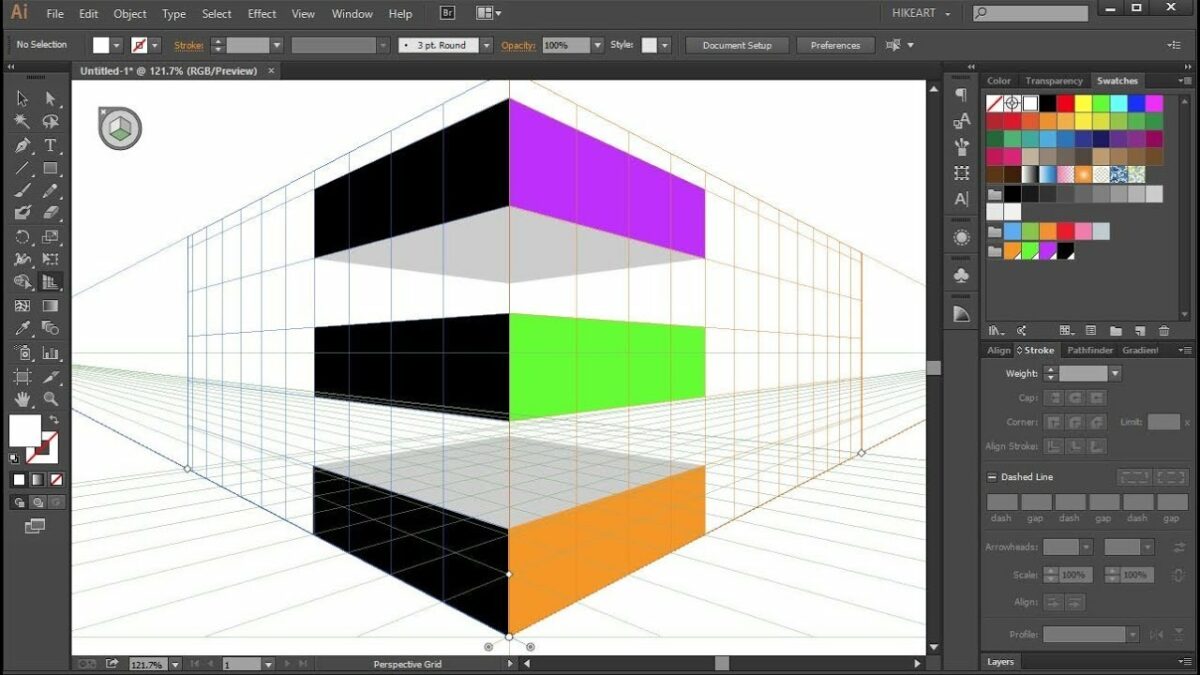
Chapter 3: Creating a Perspective Grid
With your document open in Adobe Illustrator, it’s time to create a perspective grid using the perspective grid tool. Start by activating the perspective grid tool from the toolbar or pressing Shift + P on your keyboard. Once activated, click and drag on the artboard to define the location and size of your perspective grid. Next, use the perspective grid tool panel to customize the grid’s appearance and orientation, such as adjusting the number of grid planes, setting the grid line spacing, and defining the vanishing points. Experiment with different configurations to achieve the desired perspective for your artwork.
Chapter 4: Drawing Objects in Perspective
With your perspective grid in place, it’s time to start drawing objects within the grid to create your composition. Use the pen tool, shape tools, and drawing tools in Adobe Illustrator to draw objects such as buildings, vehicles, people, and other elements of your scene directly onto the perspective grid. As you draw, pay attention to the grid lines and vanishing points to ensure that your objects maintain proper perspective and alignment within the grid. Experiment with overlapping objects, varying sizes, and changing depths to create a sense of depth and dimension in your composition.
Chapter 5: Editing and Manipulating Objects
Once you’ve drawn objects within the perspective grid, you may need to edit and manipulate them to achieve the desired look and feel. Use the selection tool (V) to select individual objects, then use the transform tools, such as the scale tool and the rotate tool, to resize, rotate, and position objects within the grid. Experiment with adjusting the perspective of objects by dragging their anchor points along the grid lines, allowing you to change their orientation and depth within the scene. Take advantage of the perspective selection tool to select and manipulate objects within specific grid planes, enabling precise control over object placement and perspective.
Chapter 6: Adding Details and Textures
To enhance the realism and depth of your perspective grid artwork, consider adding details and textures to objects within the scene. Use the appearance panel and graphic styles in Adobe Illustrator to apply gradients, patterns, and textures to objects, adding visual interest and dimension to your composition. Experiment with adding shadows, highlights, and reflections to simulate lighting and surface effects, further immersing viewers in the environment. Pay attention to details such as perspective distortion and foreshortening when applying textures and details, ensuring that they align with the spatial perspective of the grid.
Chapter 7: Incorporating Atmospheric Effects
To further enhance the depth and atmosphere of your perspective grid artwork, consider incorporating atmospheric effects such as fog, haze, or atmospheric perspective. Use the transparency panel in Adobe Illustrator to adjust the opacity and blending modes of objects within the scene, creating subtle gradients of color and tone that recede into the distance. Experiment with adding depth cues such as aerial perspective, where distant objects appear lighter and less saturated than closer objects, to create a sense of depth and distance in your composition. Pay attention to the placement and intensity of atmospheric effects to achieve the desired mood and atmosphere in your artwork.
Chapter 8: Saving and Exporting Your Perspective Grid Artwork
Once you’ve completed your perspective grid artwork in Adobe Illustrator, it’s important to save and export your artwork for sharing or distribution. Save your Illustrator document in a compatible file format, such as AI or PDF, to preserve the vector properties of your artwork. If you’re creating artwork for web or screen-based applications, consider exporting it as an SVG file for scalability and compatibility with web browsers. For print-based projects, export your artwork as a high-resolution raster image in formats such as JPEG or PNG.
Conclusion:
Mastering the perspective grid tool in Adobe Illustrator is a journey of exploration and creativity, offering endless possibilities for creating immersive and dynamic compositions that captivate and engage viewers. By understanding the techniques and tools needed to create and manipulate perspective grids, draw objects in perspective, edit and manipulate objects, add details and textures, incorporate atmospheric effects, and save and export your artwork, you’ll be able to create stunning perspective grid illustrations that transport viewers to rich and immersive environments. So grab your stylus, set your sights on the canvas, and let Adobe Illustrator become your trusted ally for bringing depth and dimension to your artistic creations.