Introduction:
In the digital era, where our devices are an integral part of daily life, the ability to locate a misplaced or lost system is crucial. Windows 10, equipped with a suite of robust features, includes “Find My Device,” a powerful tool designed to help users track and locate their devices. This comprehensive guide will meticulously walk you through the step-by-step process of using Find My Device in Windows 10, empowering you to enhance the security of your system and mitigate the stress of device loss.
- Understanding the Importance of Find My Device: Find My Device is a security feature integrated into Windows 10 that allows users to locate their devices in case they are lost or stolen. By enabling this feature, users gain peace of mind knowing they can track the location of their Windows 10 system through the Microsoft account associated with it.
- Ensuring Device Eligibility: Before diving into the Find My Device setup, ensure that your Windows 10 device is eligible for this feature. Find My Device requires the device to be running Windows 10 version 1903 or later and have location services enabled. Additionally, the device must be signed in with a Microsoft account.
- Enabling Location Services: Find My Device relies on location services to accurately track the device’s location. To enable location services, go to “Settings” in Windows 10, select “Privacy,” and then click on “Location.” Toggle the switch to turn on location services, ensuring that the device can provide its location when needed.
- Linking a Microsoft Account: To use Find My Device, your Windows 10 system must be linked to a Microsoft account. Navigate to “Settings > Accounts > Your info” and sign in with a Microsoft account if you haven’t already. Ensure that the account is set as the primary account on the device.
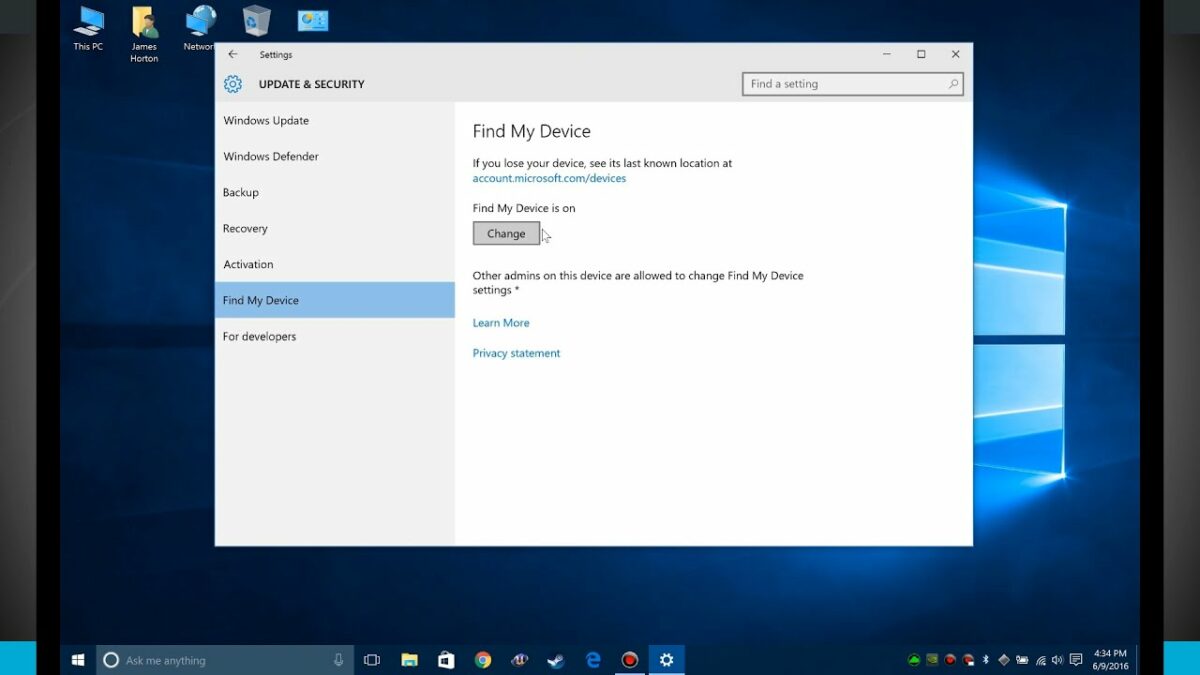
- Activating Find My Device: In the Settings menu, go to “Update & Security” and select “Find My Device” from the left-hand side. Toggle the switch to turn on Find My Device. This action activates the feature, allowing Windows 10 to track the location of the device using the associated Microsoft account.
- Accessing Find My Device Online: In the unfortunate event that your device is lost or stolen, you can use Find My Device online to track its location. Open a web browser and go to the Find My Device website (account.microsoft.com/devices). Sign in with the Microsoft account linked to the lost device.
- Locating Your Device on the Map: Once signed in, Find My Device will display a map with the last known location of your Windows 10 device. This location is determined based on the device’s recent interaction with the internet or GPS. You can zoom in on the map to pinpoint the device’s location more accurately.
- Initiating Device Actions: Find My Device offers additional actions you can take to secure your device. Click on the “Show more actions” option to reveal actions such as playing a sound (useful for locating a misplaced device), remotely locking the device, or initiating a full erase to protect sensitive data in case of theft.
- Playing a Sound to Locate Your Device: If you believe your device is nearby but cannot locate it, use the “Play a sound” option to make the device emit a distinct sound. This feature is particularly helpful when searching for a misplaced device within your home or office.
- Locking Your Device Remotely: In situations where your device is lost and security is a concern, use the “Lock” option to remotely lock your Windows 10 device. You can set a custom message on the lock screen, providing contact information for someone who may find the device.
- Erasing Data Remotely (Caution): In extreme cases of device theft or if you’re certain the device cannot be recovered, the “Erase” option allows you to remotely wipe all data from the device. Exercise caution when using this feature, as it irreversibly deletes all data on the device.
- Tracking Multiple Devices: Find My Device is not limited to a single device; it can track and manage multiple Windows 10 devices linked to the same Microsoft account. Access the Find My Device website, and use the drop-down menu to select the device you want to locate or manage.
- Accessing Find My Device on Another Windows 10 Device: In addition to using the Find My Device website, you can access the feature on another Windows 10 device. Open the Settings menu, go to “Update & Security,” and select “Find My Device.” Sign in with the Microsoft account associated with the lost device to track its location.
- Ensuring Battery and Internet Connectivity: For Find My Device to work optimally, the lost or stolen device must have an active internet connection. Additionally, the device’s battery should have sufficient charge to transmit its location. These factors play a crucial role in the accuracy and reliability of Find My Device.
- Contacting Law Enforcement (If Necessary): In the unfortunate event that your Windows 10 device is stolen, it’s advisable to contact law enforcement. Provide them with the device’s last known location and any additional information obtained through Find My Device to assist in recovery efforts.
Conclusion:
Find My Device in Windows 10 stands as a testament to the platform’s commitment to user security and peace of mind. By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, you empower yourself to navigate the stress of a lost or stolen device with confidence. Find My Device not only provides a means of locating your Windows 10 system but also offers tools to secure your data and mitigate potential risks.
As you incorporate Find My Device into your security measures, remember to keep your Microsoft account credentials secure and regularly review the status of Find My Device on your devices. By leveraging this powerful feature, Windows 10 users can safeguard their digital assets and maintain control over their devices, contributing to a more secure and resilient computing environment.