Introduction:
In the dynamic world of graphic design, CorelDRAW stands as a powerhouse, providing designers with an expansive array of tools to bring their creative visions to life. Among the multitude of features that contribute to precision and elegance in design is the ability to fillet, scallop, and chamfer corners. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of these corner manipulation techniques in CorelDRAW, exploring applications, customization options, and advanced techniques that elevate design refinement to new levels of artistry.
Understanding Fillet, Scallop, and Chamfer in CorelDRAW:
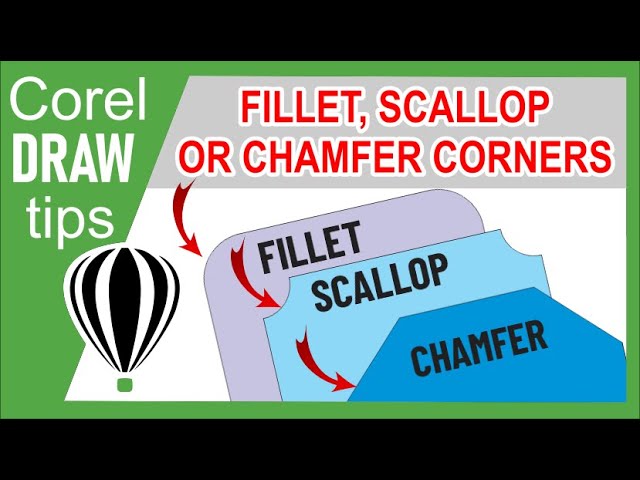
Fillet, scallop, and chamfer are corner manipulation techniques that allow designers to modify the sharpness and appearance of corners in objects. These techniques serve distinct purposes:
- Fillet:
- Fillet creates a rounded corner, smoothly connecting two straight lines. This technique is used to soften the edges of objects and add a subtle curvature to corners.
- Scallop:
- Scallop introduces a concave curve to corners, creating a series of inward curves along the edges. This technique adds a decorative and dynamic element to the corners of objects.
- Chamfer:
- Chamfer creates a beveled edge, replacing a sharp corner with a flat plane. This technique is often used for aesthetic purposes, introducing a clean and angled appearance to corners.
Accessing Fillet, Scallop, and Chamfer Tools:
CorelDRAW seamlessly integrates fillet, scallop, and chamfer tools into its interface, offering designers an intuitive means to access and apply these corner manipulation features.
- Corner Options Docker:
- The Corner Options Docker is the central hub for fillet, scallop, and chamfer settings. Designers can access this docker to choose the desired corner manipulation technique and customize parameters such as radius, intensity, and symmetry.
- Shape Tool:
- The Shape Tool plays a pivotal role in applying fillet, scallop, and chamfer to specific corners. By selecting the Shape Tool and clicking on a corner, designers can interactively manipulate corners with precision.
- Interactive Property Bar:
- The Interactive Property Bar, a dynamic toolbar that adapts to the selected tool, provides quick access to corner manipulation options. When the Shape Tool is active, designers can find relevant settings on the Interactive Property Bar for efficient adjustments.
Fillet, Scallop, and Chamfer Techniques:
Manipulating corners in CorelDRAW with fillet, scallop, and chamfer techniques encompasses a range of approaches that cater to diverse design requirements.
- Interactive Corner Manipulation:
- Interactive corner manipulation involves real-time adjustments as designers use the Shape Tool to interactively apply fillet, scallop, or chamfer to specific corners. This technique allows for dynamic and immediate modifications, ensuring precision in design refinement.
- Uniform and Variable Radius Settings:
- Designers can choose between uniform and variable radius settings for corner manipulation. Uniform settings apply the same radius to all corners, while variable settings allow for customized radius values for individual corners.
- Symmetrical Corner Manipulation:
- Symmetrical corner manipulation ensures that changes to one corner are mirrored on the opposite corner of the object. This technique is valuable for achieving balanced and harmonious designs with consistent corner treatments.
Customization Options:
CorelDRAW enhances the corner manipulation process by offering customization options that cater to the specific needs of each design.
- Precision Settings:
- Designers can customize the precision of corner manipulation by adjusting parameters such as grid options, snap settings, and measurement units. This customization option ensures accuracy when applying fillet, scallop, or chamfer to corners.
- Undo and Redo Functionality:
- The ability to undo and redo corner manipulation actions ensures a non-destructive and iterative design process. Designers can experiment with corner treatments, refining their designs with confidence.
- Custom Corner Styles:
- CorelDRAW allows designers to create custom corner styles, enabling a tailored approach to design refinement. By defining unique corner styles, designers can achieve intricate and personalized corner treatments, adding a layer of creativity to the process.
Advanced Techniques and Applications:
Beyond the basics, CorelDRAW empowers designers to explore advanced techniques for corner manipulation, unlocking new dimensions of precision and creativity.
- Layered Corner Manipulation:
- The layered corner manipulation technique involves applying multiple corner manipulation actions to different layers or objects within a design. By combining various corner treatments, designers can achieve complex compositions, creating designs with intricate and dynamic layering.
- Corner Manipulation in Typography:
- Corner manipulation is valuable when working with typography, allowing designers to refine and customize letterforms with precision. Whether applying fillet to soften letter edges or chamfer for a modern aesthetic, designers can achieve polished and unique typography.
- Patterned Corner Treatments:
- Designers can utilize patterned corner treatments to create visually interesting designs. By defining custom patterns for corner manipulation, designers can add texture and detail to their designs, resulting in visually captivating and intricate compositions.
Applications in Various Design Disciplines:
The ability to fillet, scallop, and chamfer corners in CorelDRAW finds diverse applications across design disciplines, showcasing its adaptability and versatility.
- Logo Design and Branding:
- In logo design and branding, corner manipulation is crucial for creating distinct and memorable visual identities. Designers can use fillet, scallop, or chamfer to add a unique touch to logo corners, contributing to brand recognition.
- Architectural and Technical Illustrations:
- Corner manipulation is valuable in architectural and technical illustrations, allowing designers to add a touch of style to precise drawings. This technique contributes to the creation of visually appealing and informative technical illustrations.
- Product Design and Packaging:
- The ability to manipulate corners is indispensable in product design and packaging. Designers can use these techniques to add a refined and sophisticated look to product shapes and packaging designs, enhancing visual appeal.
- Digital Illustrations and Artwork:
- In digital illustrations, corner manipulation allows for the creation of intricate and detailed compositions. Designers can use these techniques to refine shapes, add decorative elements, and achieve polished and visually striking digital artworks.
- Web and User Interface Design:
- Corner manipulation is beneficial in web and user interface design, allowing designers to create clean and visually appealing layouts. Whether applying fillet to soften interface elements or chamfer for a modern look, designers can enhance the user experience through thoughtful corner treatments.
Conclusion:
Fillet, scallop, and chamfer corners in CorelDRAW are essential techniques that empower designers to achieve precision, elegance, and uniqueness in their digital designs. Whether working on logos, technical illustrations, product designs, or digital artworks, designers rely on these techniques to bring their visions to life with artistry and sophistication.
As designers continue to explore the extensive capabilities of CorelDRAW’s corner manipulation tools, they unlock new dimensions of creative freedom and precision. The ability to fillet, scallop, and chamfer corners with confidence allows designers to navigate the complexities of graphic design, transforming concepts into visually captivating and artistically expressive artworks. CorelDRAW, with its intuitive interface and powerful corner manipulation features, remains an indispensable tool for designers seeking to achieve both precision and creativity in their digital compositions.