Understanding Lambda Functions
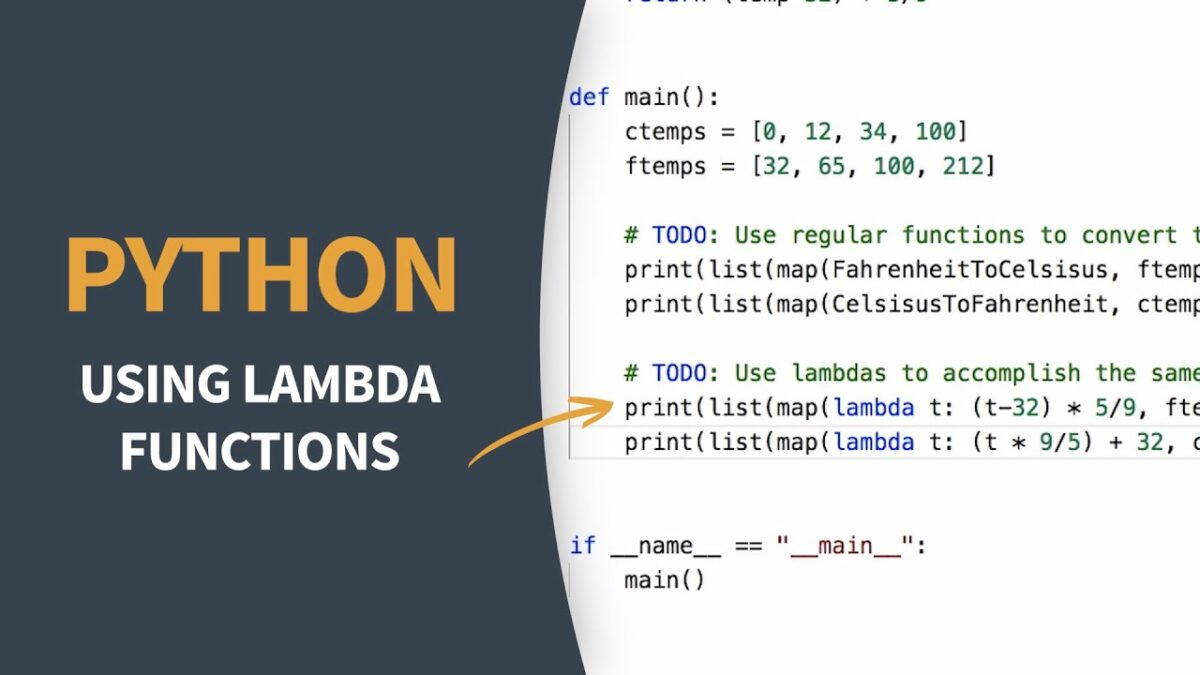
Lambda functions, also known as anonymous functions, are concise expressions used to create small, one-time-use functions in Python. They are defined using the lambda keyword, followed by arguments, a colon, and an expression.
Syntax
lambda arguments: expression
lambda: Keyword to define a lambda function.arguments: Comma-separated list of parameters.expression: The function’s body, which returns a value.
Basic Example
double = lambda x: x * 2
result = double(5)
print(result) # Output: 10
Multiple Arguments
Lambda functions can take multiple arguments:
add = lambda x, y: x + y
result = add(3, 4)
print(result) # Output: 7
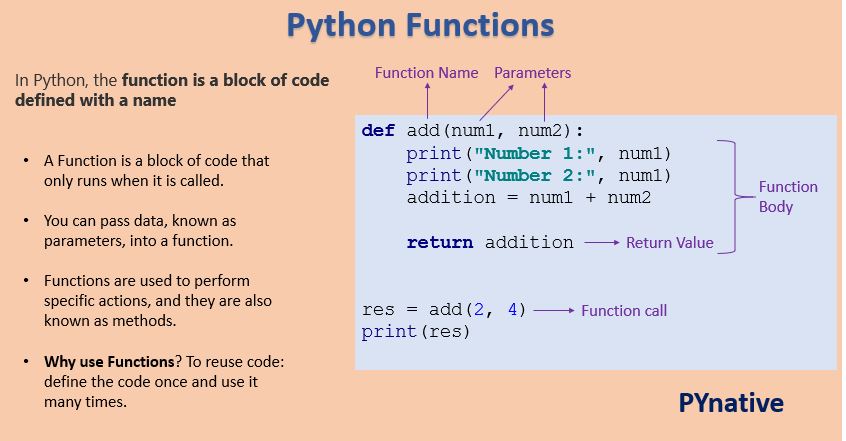
Limitations of Lambda Functions
- Single Expression: Lambda functions can only contain a single expression.
- No Statements: They cannot contain statements like
if,for, orwhile. - Limited Readability: For complex logic, regular functions are often preferred.
Use Cases for Lambda Functions
While lambda functions have limitations, they are valuable in specific scenarios:
- Short, Simple Functions: When you need a small function for a one-time use.
- Higher-Order Functions: As arguments to functions like
map,filter, andreduce. - Inline Functions: When you need a function directly within another expression.
Lambda Functions with Higher-Order Functions
Lambda functions shine when combined with higher-order functions:
map()
Applies a function to each item of an iterable and returns an iterator:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared = map(lambda x: x * x, numbers)
print(list(squared)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
filter()
Creates an iterator containing elements from an iterable for which a function returns True:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
even_numbers = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers)
print(list(even_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4]
reduce()
Applies a function of two arguments cumulatively to the items of an iterable, from left to right, so as to reduce the iterable to a single value:
from functools import reduce
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
product = reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, numbers)
print(product) # Output: 24
Lambda Functions with sorted()
You can use lambda functions as the key argument in the sorted() function for custom sorting:
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David']
sorted_names = sorted(names, key=lambda x: len(x))
print(sorted_names) # Output: ['Bob', 'Alice', 'David', 'Charlie']
Lambda Functions with key Argument in Dictionaries
You can use lambda functions as the key argument in dictionary methods like sorted() and max():
students = {'Alice': 95, 'Bob': 88, 'Charlie': 92}
top_student = max(students, key=lambda k: students[k])
print(top_student) # Output: Alice
Best Practices for Using Lambda Functions
- Keep lambda functions simple and concise.
- Use them judiciously, not for complex logic.
- Consider naming lambda functions for better readability if they are used multiple times.
- Use regular functions for more complex operations.
Advanced Topics
- Lambda functions with default arguments
- Nested lambda functions
- Lambda functions as closures
- Performance implications of lambda functions
By understanding lambda functions and their applications, you can write more concise and expressive Python code.