In the expansive landscape of academic writing, citations and bibliographies play a crucial role in acknowledging sources, providing credibility, and facilitating further research. Whether you’re writing a research paper, thesis, or scholarly article, a well-constructed bibliography is essential for documenting your sources and allowing readers to explore the cited works in-depth. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of creating bibliographies in Microsoft Word, empowering you to manage citations with precision and ease, and adhere to citation style guidelines with confidence.
Understanding the Significance of Bibliographies:
Before delving into the practical aspects of creating bibliographies, it’s crucial to grasp the significance of these scholarly components in academic writing. Bibliographies serve multiple purposes, including:
- Providing credit to sources: Bibliographies acknowledge the intellectual contributions of authors and researchers whose work has influenced or contributed to your own.
- Facilitating verification: By listing the sources consulted and cited in your work, bibliographies enable readers to verify the accuracy and reliability of your research.
- Supporting further exploration: Bibliographies serve as valuable resources for readers seeking to explore related literature, conduct further research, or delve deeper into specific topics.
By incorporating bibliographies into your academic writing workflow, you can enhance the credibility, transparency, and accessibility of your research findings and contribute to the scholarly discourse in your field.
Basic Bibliography Creation:
Creating a bibliography in Microsoft Word is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using built-in tools and features. Here’s how to do it:
- Insert Citations:
- As you write your document, insert citations for each source using Word’s built-in citation manager or a citation management tool such as Zotero or EndNote.
- Place your cursor at the location where you want to insert the citation, then navigate to the “References” tab and click on “Insert Citation.”
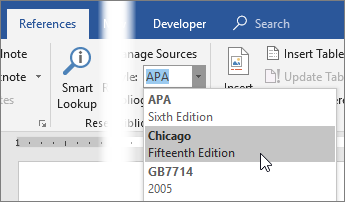
- Choose Citation Style:
- Before inserting citations, specify the citation style you wish to use for your document. Common styles include APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard.
- In the “References” tab, click on the “Style” dropdown menu and choose the desired citation style.
- Add New Sources:
- If citing sources that haven’t been added to your bibliography yet, click on “Manage Sources” in the citation manager to add new sources manually or import them from external databases.
- Generate Bibliography:
- Once you’ve inserted all your citations, place your cursor at the end of your document where you want the bibliography to appear.
- Navigate to the “References” tab, click on “Bibliography,” and choose the appropriate bibliography style (e.g., “Bibliography” for a full list of sources, “Works Cited” for MLA style, or “References” for APA style).
Advanced Bibliography Management:
While basic bibliography creation suffices for most scenarios, Microsoft Word offers advanced features and customization options to further enhance the appearance and functionality of bibliographies. Here are some additional features you may explore:
- Customize Citation Styles:
- Word allows users to customize citation styles by modifying the formatting of citations and bibliographies according to specific requirements or publisher guidelines.
- Access the “Manage Sources” and “Citation Style” options to customize citation styles or create new styles based on existing templates.
- Sort and Organize Entries:
- Word enables users to sort and organize bibliography entries alphabetically, chronologically, or by other criteria to enhance readability and accessibility.
- Use the sorting and filtering options in the citation manager to arrange entries according to your preferences.
- Update Citations and Bibliography:
- As you revise and edit your document, ensure that citations and bibliographic entries are kept up-to-date with any changes or additions.
- Use the “Update Citations and Bibliography” option in the “References” tab to refresh citations and bibliography entries automatically.
Best Practices for Bibliography Management:
While creating a bibliography in Microsoft Word is relatively straightforward, it’s essential to adhere to best practices for citation and bibliography management to ensure accuracy, consistency, and professionalism. Here are some tips to consider:
- Consult Citation Style Guides:
- Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements and guidelines of the citation style(s) preferred or mandated by your academic institution, publisher, or discipline.
- Consult authoritative style guides such as the APA Publication Manual, MLA Handbook, or Chicago Manual of Style for detailed instructions on citation formatting.
- Verify Sources and Formatting:
- Double-check the accuracy of each citation and bibliographic entry, including author names, publication dates, titles, and page numbers, to ensure consistency and correctness.
- Pay attention to punctuation, capitalization, and formatting conventions prescribed by the chosen citation style.
- Use Citation Management Tools:
- Consider using citation management tools such as Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote to streamline the citation and bibliography management process, organize your research library, and generate citations automatically.
- Review and Revise Regularly:
- Periodically review and revise your bibliography to incorporate any new sources, updates, or corrections. Maintain a meticulous approach to citation and bibliography management throughout the writing process.
Conclusion:
Creating a bibliography in Microsoft Word is an essential skill for academic writers, researchers, and students seeking to document their sources accurately, acknowledge intellectual contributions, and contribute to the scholarly discourse in their field. By mastering the basic citation insertion process, exploring advanced bibliography management options, and adhering to best practices for citation formatting and documentation, you can create bibliographies that enhance the credibility, transparency, and professionalism of your academic work. Whether you’re writing a research paper, dissertation, or journal article, a well-constructed bibliography serves as a testament to your diligence, integrity, and commitment to scholarly excellence. So, the next time you embark on an academic writing endeavor in Word, remember to leverage the power of bibliographies to document your sources, support your arguments, and engage with the scholarly community in a meaningful and responsible manner.