Congratulations on your new Windows 10 device! Whether it’s a brand-new PC, laptop, or tablet, setting up Windows 10 for the first time is an exciting step towards unleashing its full potential. In this extensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of setting up your Windows 10 device right out of the box, from initial configuration to personalization and optimization. By following these steps, you’ll be able to get your device up and running smoothly and customize it to suit your preferences and needs.
Step 1: Power On and Initial Setup:
- Unboxing: Carefully unpack your new Windows 10 device, ensuring that all accessories and components are present and undamaged.
- Power On: Press the power button to turn on your device and initiate the initial setup process.
- Language and Region: Select your preferred language, region, and keyboard layout to configure your device for your location and language preferences.
- Connect to Wi-Fi: Connect your device to a Wi-Fi network to enable internet access and facilitate the setup process.
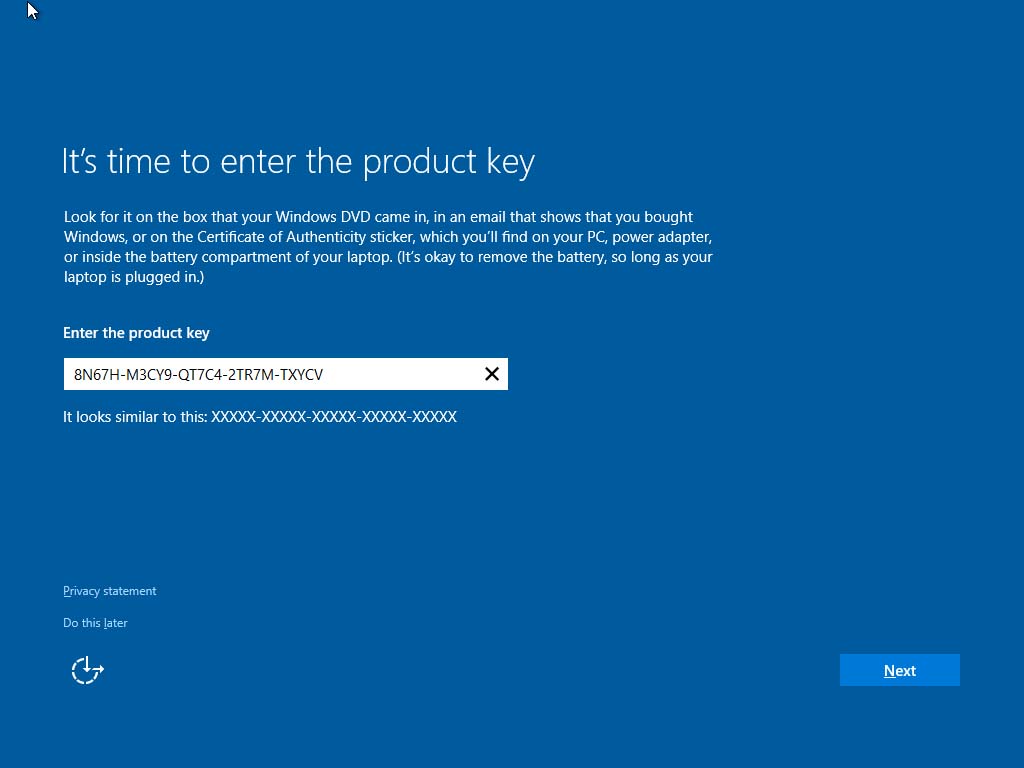
- Sign in with Microsoft Account: Sign in with your Microsoft account or create a new one if you don’t have an existing account. Your Microsoft account allows you to access various Microsoft services and sync your settings across devices.
- Privacy Settings: Review and customize your privacy settings according to your preferences. Choose whether to enable or disable features such as location tracking, diagnostic data collection, and personalized advertising.
Step 2: Personalization and Customization:
- Choose PC Name: Assign a unique name to your device to distinguish it from other devices on your network.
- Set Up Security: Set up security options such as a PIN, password, or biometric authentication (if available) to protect your device and data from unauthorized access.
- Customize Start Menu: Customize the Start menu layout by pinning your favorite apps, resizing tiles, and organizing them into groups for easy access.
- Select Theme and Background: Personalize the desktop background, theme colors, and accent settings to customize the appearance of your device.
- Configure Notifications: Manage notification settings to control which apps can send notifications and how they are displayed on your device.
Step 3: Install Essential Apps and Software:
- Windows Updates: Check for and install any available Windows updates to ensure that your device has the latest security patches and improvements.
- Microsoft Store: Explore the Microsoft Store to discover and install essential apps and software for productivity, entertainment, and creativity.
- Antivirus Software: Install reputable antivirus software to protect your device from malware, viruses, and other online threats.
- Productivity Tools: Install productivity tools such as Microsoft Office, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams to enhance your work efficiency and collaboration.
- Web Browser: Choose and set up a web browser that suits your preferences, whether it’s Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, or Mozilla Firefox.
Step 4: Backup and Data Migration:
- Data Backup: Set up a backup system to protect your important files and documents from loss or corruption. Use built-in tools like File History or third-party backup software for automatic backups.
- Data Migration: Transfer your files, photos, and documents from your old device to your new Windows 10 device using methods such as external storage devices, cloud storage, or network transfer.
Step 5: Optimize Performance and Settings:
- System Optimization: Optimize system performance by adjusting settings such as power management, visual effects, and startup programs to improve speed and responsiveness.
- Device Settings: Customize device settings such as display resolution, sound preferences, and touchpad sensitivity to suit your preferences and usage habits.
- Security Settings: Review and configure security settings such as Windows Defender, firewall settings, and app permissions to enhance device security and protect your privacy.
- Accessibility Options: Explore accessibility options and settings to customize your device for individuals with specific needs or preferences, such as magnifier, narrator, and closed captions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, setting up your new Windows 10 device out of the box is an exciting process that allows you to personalize and customize your computing experience to suit your preferences and needs. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can get your device up and running smoothly, install essential apps and software, and optimize settings for optimal performance and usability. So go ahead, embark on your Windows 10 journey, and make the most of your new device by setting it up just the way you like it!