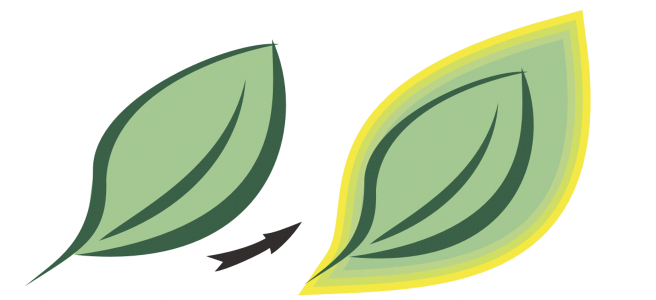
Introduction:
In the dynamic realm of graphic design, the art of contouring objects stands as a fundamental technique, elevating designs from two-dimensional compositions to visually engaging masterpieces. CorelDRAW, a cornerstone in graphic design software, introduces a versatile toolkit, and within it, the ability to contour objects emerges as a powerful feature. In this extensive guide, we embark on a comprehensive exploration of contouring objects in CorelDRAW, unraveling their functionalities, applications, and the transformative impact they bring to the creative process.
Understanding Contouring Objects in CorelDRAW:
- Contours as Design Alchemy: Contouring objects in CorelDRAW represents a form of design alchemy, where designers can shape, enhance, and define their creations with precision. Contours become a conduit for artistic expression, offering a spectrum of creative possibilities to elevate designs.
- Versatility in Contouring: CorelDRAW’s contouring capabilities offer a versatile range of options, enabling designers to add depth, create dynamic effects, and emphasize specific elements within their designs. This toolkit serves as a canvas for creative exploration, allowing for the creation of designs that transcend traditional boundaries.
- Advantages of Contouring Objects: Contouring objects provides designers with a host of advantages, including the ability to add visual interest, create three-dimensional effects, and enhance the overall composition. These contouring capabilities serve as a powerful tool for designers seeking to bring depth and dimensionality to their designs.
Basic Contouring Techniques:
- Outer Contours for Emphasis: CorelDRAW’s contouring capabilities include fundamental tools for adding outer contours to objects. Designers can use this technique to emphasize the edges of shapes, text, or graphics, creating a visually striking effect.
- Inner Contours for Depth: Designers can explore inner contouring techniques, adding depth to objects by creating concentric shapes within them. This technique is valuable for creating a sense of dimensionality and visual hierarchy within designs.
Dynamic Contour Enhancements:
- Interactive Real-time Contouring: CorelDRAW’s contouring capabilities extend to interactive real-time adjustments, enabling designers to contour objects and observe changes instantly. This dynamic approach fosters experimentation and facilitates on-the-fly refinements.
- Contour Variations with PowerClip: Designers can leverage PowerClip features in conjunction with contouring, allowing for variations in how contours interact with objects. This technique is particularly useful for intricate designs and detailed compositions.
Artistic Contour Manipulations:
- Abstract Contour Artwork: Contouring objects empowers designers to create abstract contour artwork, experimenting with unconventional combinations of shapes and contours. This technique allows for the exploration of intricate and avant-garde design elements.
- Layered Contour Compositions: Designers can use contouring tools to create layered compositions, applying multiple contours to objects to produce visually intriguing designs. This technique adds a multidimensional quality to flat images.
Practical Applications of Contouring Objects:
- Logo Design and Branding: Contouring objects play a pivotal role in logo design and branding, where creating memorable and visually distinctive marks is crucial. Designers can use these capabilities to add depth and sophistication to brand identities.
- Digital Illustrations and Artwork: In the realm of digital illustrations and artwork, contouring objects are indispensable for creating lifelike and immersive compositions. Designers can use these capabilities to add realism and dimension to their digital creations.
Advanced Contouring Techniques:
- Custom Contour Creation: CorelDRAW’s advanced contouring capabilities include tools for creating custom contours. This advanced technique allows designers to craft unique contour effects that align with the specific theme or narrative of their design.
- Contouring with Variable Width: Designers can explore contouring with variable width techniques within CorelDRAW, allowing for variations in the thickness of contours. This advanced method adds a dynamic and expressive element to designs.
Customization and Fine-Tuning:
- Control over Contour Parameters: Designers have granular control over the parameters of contoured objects, including contour width, color, and spacing. This level of control ensures that designers can precisely customize the impact of contours on different elements in their designs.
- Real-time Previews: The real-time preview feature in CorelDRAW enables designers to observe the impact of contoured objects instantly. This iterative process facilitates experimentation and allows designers to make informed decisions about the application of contour effects.
Combining Contoured Objects with Other Tools:
- Integration with CorelDRAW Tools: Contoured objects seamlessly integrate with other CorelDRAW tools and functionalities. Designers can combine the application of contours with vector elements, text, and other design components to create cohesive and visually striking compositions.
- Layering and Masking Techniques: CorelDRAW allows designers to use layering and masking techniques in conjunction with contoured objects. This synergy enables the creation of complex visual compositions with seamless transitions and layered contour effects.
Collaboration and File Sharing:
- Compatibility Across Versions: When collaborating on projects involving contoured objects, designers should ensure compatibility across different versions of CorelDRAW. This guarantees that contour effects are applied consistently, regardless of the software version used.
- Exporting Designs with Contour Effects: Designers can export designs with applied contour effects, ensuring that the enhanced depth and dimensionality are retained when sharing files with clients, collaborators, or across different platforms.
Best Practices and Tips:
- Purposeful Contour Application: Successful contouring involves purposeful application. Designers should consider the overall design context and narrative, using contours to enhance specific elements and contribute positively to the visual storytelling.
- Experimentation with Contour Variations: Experimenting with different contour variations can lead to unexpected and visually appealing results. Designers are encouraged to explore diverse contour effects and experiment with their combinations to discover unique and captivating enhancements.
Conclusion:
Contouring objects in CorelDRAW opens a gateway to a realm where designs transcend the ordinary and become visually enriched compositions. From emphasizing edges to creating intricate layered effects, contouring capabilities offer designers the opportunity to shape their creations with precision and artistic finesse. As the design landscape continues to evolve, contouring objects in CorelDRAW stands as a testament to the software’s commitment to providing designers with tools that inspire innovation and imaginative expression. Mastering the art of contouring invites designers to explore a realm where every contour is a stroke of creativity, contributing to the visual narrative with depth, sophistication, and an unparalleled artistic appeal.