The INDIRECT function in Excel is a powerful and versatile tool that allows users to create dynamic references to cells, ranges, or named ranges using text strings. This function can be particularly useful in scenarios where cell references need to be generated dynamically based on certain criteria or conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about using the INDIRECT function in Excel, from basic syntax to advanced techniques and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Using the INDIRECT Function
- Basic Syntax and Usage
- Practical Examples
- Using Cell References
- Creating Dynamic Range References
- Referencing Named Ranges
- Advanced Techniques
- Using INDIRECT with Other Functions
- Dynamic Worksheet References
- Conditional Dynamic References
- Handling Errors
- Common Errors and Troubleshooting
- Ensuring Data Integrity
- Tips and Tricks
- Using Text Manipulation Functions
- Utilizing Named Ranges
- Dynamic Charting
- Real-World Applications
- Financial Modeling
- Data Analysis
- Reporting
- Best Practices
- Documenting Formulas
- Validating Indirect References
- Regularly Testing Formulas
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The INDIRECT function in Excel provides a way to indirectly reference cells, ranges, or named ranges based on text strings. This can be particularly useful when dealing with dynamic data or when the exact cell reference is not known in advance. By using the INDIRECT function, users can create flexible and dynamic formulas that adapt to changes in the underlying data.
2. Benefits of Using the INDIRECT Function
- Dynamic References: Create references to cells or ranges dynamically based on text strings.
- Versatility: Use INDIRECT to reference cells across different worksheets or workbooks.
- Simplicity: Simplify complex formulas by dynamically generating cell references.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks by using INDIRECT to create dynamic formulas.
3. Basic Syntax and Usage
The basic syntax of the INDIRECT function is as follows:
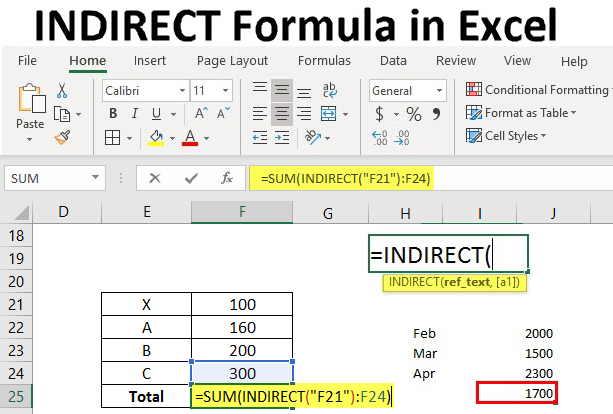
=INDIRECT(ref_text, [a1])
- ref_text: The text string that represents the cell reference, range reference, or named range.
- a1: Optional. A logical value that specifies the reference style. TRUE or omitted indicates A1 style reference, FALSE indicates R1C1 style reference.
4. Practical Examples
Using Cell References
To reference a cell dynamically based on a text string:
=INDIRECT("A1")
Creating Dynamic Range References
To create a dynamic range reference based on a text string:
=INDIRECT("A1:A10")
Referencing Named Ranges
To reference a named range dynamically:
=INDIRECT("SalesData")
5. Advanced Techniques
Using INDIRECT with Other Functions
Combine INDIRECT with other functions to create more complex formulas. For example:
=SUM(INDIRECT("A1:A10"))
Dynamic Worksheet References
To reference cells or ranges on different worksheets dynamically:
=INDIRECT("'Sheet2'!A1")
Conditional Dynamic References
Create dynamic references based on conditions. For example:
=IF(condition, INDIRECT("A1"), INDIRECT("B1"))
6. Handling Errors
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
- #REF! Error: This error occurs if the specified reference is not valid.
- #VALUE! Error: This error occurs if the ref_text argument is not a valid reference.
- Circular Reference: Be cautious of circular references when using INDIRECT, as they can cause calculation errors.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Regularly review formulas containing INDIRECT to ensure that references remain valid, especially if the structure of the worksheet changes.
7. Tips and Tricks
Using Text Manipulation Functions
Combine INDIRECT with text manipulation functions like CONCATENATE or TEXT to create dynamic references programmatically.
Utilizing Named Ranges
Use named ranges in conjunction with INDIRECT to create more readable and maintainable formulas.
Dynamic Charting
Create dynamic charts that update automatically based on user-selected criteria using INDIRECT to reference data ranges.
8. Real-World Applications
Financial Modeling
Use INDIRECT to dynamically reference financial data across different worksheets or workbooks in financial models.
Data Analysis
Create dynamic formulas that reference data based on user input, allowing for interactive data analysis.
Reporting
Build dynamic reports that update automatically based on changes to underlying data using INDIRECT to reference data ranges.
9. Best Practices
Documenting Formulas
Document formulas containing INDIRECT to provide context and aid understanding for other users.
Validating Indirect References
Regularly validate indirect references to ensure that they remain accurate and up-to-date as the structure of the worksheet changes.
Regularly Testing Formulas
Regularly test formulas containing INDIRECT to ensure that they produce the expected results under various conditions.
10. Conclusion
The INDIRECT function in Excel is a powerful tool for creating dynamic references to cells, ranges, or named ranges based on text strings. By mastering the basic syntax and exploring advanced techniques, users can leverage the flexibility of INDIRECT to create more versatile and efficient formulas. Whether used for financial modeling, data analysis, or reporting, INDIRECT provides a way to create dynamic and adaptable solutions that can meet a wide range of needs.
By incorporating INDIRECT into their Excel workflows and following best practices for formula documentation, validation, and testing, users can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their spreadsheets. With its versatility and flexibility, the INDIRECT function opens up new possibilities for creating dynamic and interactive Excel applications that can enhance productivity and streamline workflows.