Introduction: In the vast landscape of social media, fostering a safe and respectful environment is essential for the well-being of users and the integrity of the platform. Instagram, one of the world’s most popular social media platforms, provides users with tools and resources to report content that violates community guidelines, promotes harmful behavior, or infringes on the rights of others. Reporting a post on Instagram is a proactive step towards upholding community standards, combating online abuse, and ensuring a positive experience for all users. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about reporting a post on Instagram, from understanding when to report to step-by-step instructions for filing a report, as well as tips for navigating the reporting process and contributing to a safer online community.
Understanding When to Report a Post on Instagram
Reporting a post on Instagram is a responsibility that should be exercised thoughtfully and in accordance with community guidelines. You may choose to report a post if:
- It contains hate speech, harassment, or threats directed towards individuals or groups based on factors such as race, ethnicity, gender, religion, or sexual orientation.
- It promotes violence, self-harm, or dangerous behavior that poses a risk to the safety or well-being of others.
- It infringes on intellectual property rights, such as copyright or trademark violations.
- It contains explicit or graphic content that is not suitable for all audiences, including nudity, violence, or graphic imagery.
- It engages in spamming, phishing, or other forms of fraudulent or deceptive behavior.
Reporting a post on Instagram is an important mechanism for flagging inappropriate or harmful content and helping to maintain a positive and respectful online community.
How to Report a Post on Instagram
Reporting a post on Instagram is a straightforward process that can be done in a few simple steps:
- Open the Instagram App: Launch the Instagram app on your mobile device and log in to your account if you haven’t already done so.
- Navigate to the Post: Find the post you want to report. You can do this by scrolling through your feed, exploring hashtags, or visiting the profile of the user who posted it.
- Access the Options Menu: Tap on the three dots (ellipsis) in the top right corner of the post. This will open a menu of options for interacting with the post.
- Select “Report”: From the menu of options, tap on “Report.” Instagram will prompt you to select the reason for your report from a list of options.
- Choose a Reason: Select the reason that best describes why you’re reporting the post. Options may include “It’s inappropriate,” “It’s spam,” “It’s abusive or harmful,” or “It promotes violence or harm.”
- Provide Additional Details (Optional): If desired, you can provide additional information or context to support your report. This may include specific details about why the post violates community guidelines or poses a risk to users.
- Submit the Report: After selecting the reason for your report and providing any additional details, tap on “Submit Report” to file your report with Instagram.
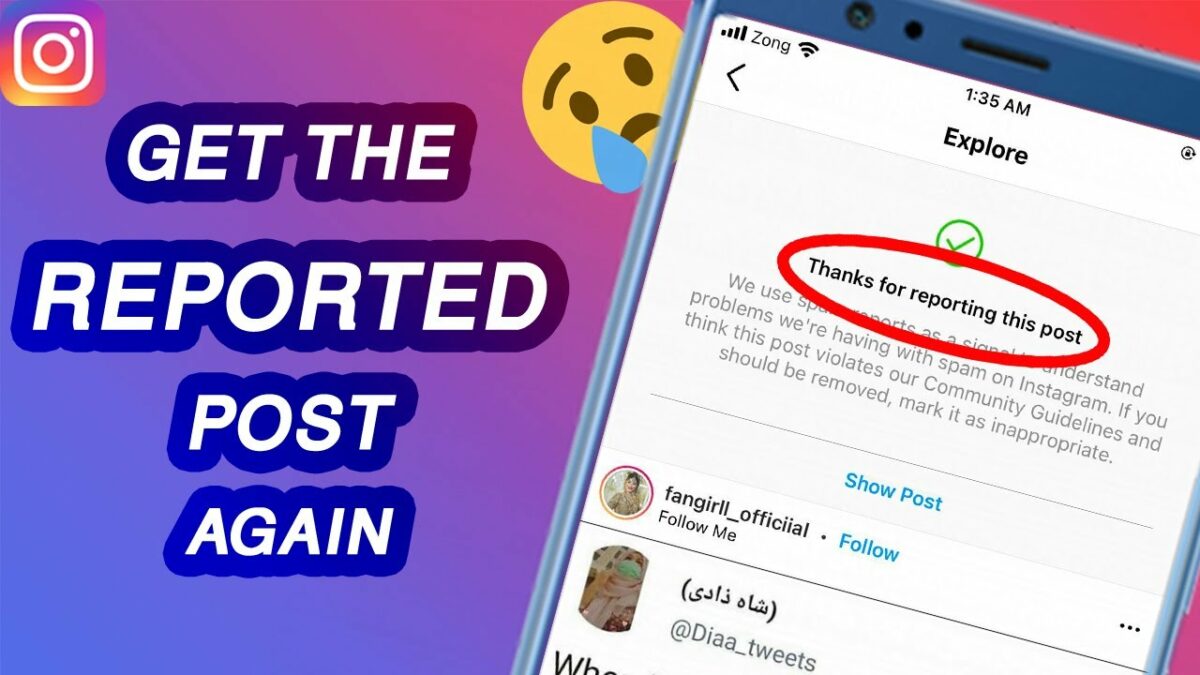
- Confirmation Message: Instagram will display a confirmation message indicating that your report has been submitted. You may also receive a follow-up notification if Instagram takes action based on your report.
Tips for Navigating the Reporting Process on Instagram
- Familiarize Yourself with Community Guidelines: Before reporting a post, familiarize yourself with Instagram’s community guidelines to ensure that your report aligns with platform standards.
- Be Specific and Detailed: When filing a report, provide specific details and examples to support your concerns. This will help Instagram moderators understand the nature of the violation and take appropriate action.
- Use the Right Reporting Option: Instagram offers different reporting options for various types of content violations, such as reporting individual posts, profiles, comments, or direct messages. Choose the reporting option that best matches the nature of the violation.
- Report Violations Promptly: If you encounter content that violates community guidelines, report it promptly to ensure timely action by Instagram moderators.
- Monitor Reporting Outcomes: After filing a report, monitor the outcome to see if Instagram takes action, such as removing the reported content or taking disciplinary action against the offending account.
- Contribute to a Safer Community: Reporting inappropriate or harmful content on Instagram is not only about protecting yourself but also about contributing to a safer and more positive community for all users.
Conclusion
Reporting a post on Instagram is a proactive step towards upholding community standards, promoting safety, and fostering a positive online environment. By understanding when to report, following the step-by-step instructions for filing a report, and implementing tips for navigating the reporting process, you can contribute to a safer and more respectful community on Instagram. So, if you encounter content that violates community guidelines or poses a risk to users, don’t hesitate to speak up and report it. Together, we can work towards creating a digital space where everyone feels safe, respected, and valued.