In the realm of computer troubleshooting, encountering a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) can be a daunting experience, signaling a critical system error that requires immediate attention. Blue screen errors in Windows XP, often accompanied by cryptic error codes and technical jargon, can leave users feeling frustrated and uncertain about how to proceed. However, with the right knowledge and tools at hand, troubleshooting blue screen errors in Windows XP can be a manageable task. In this exhaustive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of blue screen error troubleshooting, empowering users to diagnose and resolve these issues with confidence and precision.
Understanding Blue Screen Errors in Windows XP:
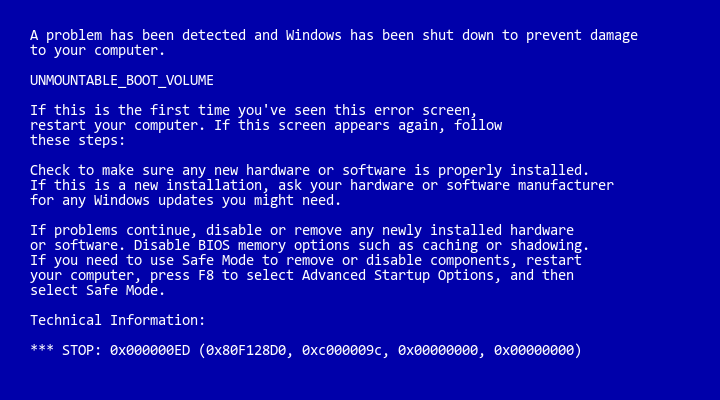
Before we delve into the troubleshooting process, it’s essential to understand the nature of blue screen errors in Windows XP. A blue screen error, also known as a STOP error or a kernel panic, occurs when the operating system encounters a critical system error that it cannot recover from. This results in the system displaying a blue screen with error information, including error codes, technical details, and possibly the name of the offending driver or module. Blue screen errors can occur due to various reasons, including hardware issues, driver conflicts, software bugs, and system corruption.
Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting Blue Screen Errors:
Now, let’s explore a systematic approach to troubleshooting blue screen errors in Windows XP:
Step 1: Note Down Error Information:
- When a blue screen error occurs, take note of the error message displayed on the screen, including any error codes or technical details.
- Pay attention to any recent changes or events that may have preceded the blue screen error, such as hardware installations, driver updates, or software installations.
Step 2: Restart the Computer:
- If the blue screen error is preventing the computer from functioning, restart the system by pressing the reset button or holding down the power button until the system powers off.
- Allow the system to restart and attempt to boot into Windows XP.
Step 3: Boot into Safe Mode:
- If the system fails to boot into Windows XP normally due to the blue screen error, attempt to boot into Safe Mode by pressing the F8 key repeatedly during startup.
- In Safe Mode, Windows XP loads with minimal drivers and services, allowing for troubleshooting and diagnostic purposes.
Step 4: Identify and Resolve Hardware Issues:
- Blue screen errors can often be caused by hardware issues such as faulty RAM, overheating components, or failing hard drives.
- Perform a thorough inspection of the hardware components, including RAM modules, CPU cooling system, and hard drive connections.
- Test hardware components using diagnostic tools such as MemTest86 for RAM testing or CrystalDiskInfo for hard drive health monitoring.
- Replace or repair any faulty hardware components identified during the diagnostic process.
Step 5: Update Device Drivers:
- Outdated or incompatible device drivers can also cause blue screen errors in Windows XP.
- Use Device Manager to identify devices with outdated drivers or drivers showing error status.
- Download and install the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website for each affected device.
- Alternatively, use third-party driver update software to automate the driver update process.
Step 6: Check for Software Issues:
- Blue screen errors can sometimes be triggered by software conflicts, malware infections, or system corruption.
- Perform a thorough malware scan using reputable antivirus or antimalware software to detect and remove any malicious programs.
- Use System File Checker (SFC) to scan for and repair corrupted system files. Open a Command Prompt window and type “sfc /scannow” to initiate the scan.
- Uninstall recently installed or problematic software applications using Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel.
Step 7: Analyze Blue Screen Dump Files:
- Windows XP generates dump files (.dmp) when a blue screen error occurs, containing valuable diagnostic information.
- Use a debugging tool such as WinDbg (Windows Debugger) to analyze the dump files and identify the cause of the blue screen error.
- Analyze the dump file for error codes, stack traces, and module information to pinpoint the offending driver or component.
Step 8: Restore System to a Previous State:
- If troubleshooting efforts fail to resolve the blue screen error, consider restoring the system to a previous restore point using System Restore.
- Boot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt and type “rstrui.exe” to launch the System Restore wizard.
- Follow the prompts to select a restore point dated before the occurrence of the blue screen error and initiate the restoration process.
Step 9: Perform a Repair Installation of Windows XP:
- As a last resort, consider performing a repair installation of Windows XP to repair corrupted system files and restore system stability.
- Boot from the Windows XP installation disc and follow the prompts to initiate the repair installation process.
- Ensure to select the “Repair” or “Reinstall” option when prompted, rather than the “Install” option, to preserve existing data and settings.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, troubleshooting blue screen errors in Windows XP requires a systematic approach, patience, and a good understanding of the underlying causes of such errors. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article and leveraging diagnostic tools and techniques, users can effectively diagnose and resolve blue screen errors, restoring system stability and ensuring smooth operation. Whether addressing hardware issues, updating device drivers, or analyzing dump files, mastering the art of blue screen error troubleshooting empowers users to maintain peak performance and reliability of their Windows XP systems. So equip yourself with the knowledge and tools needed to tackle blue screen errors with confidence, and ensure a seamless computing experience on your Windows XP machine.