Introduction:
CorelDRAW, a powerhouse in the realm of graphic design, provides designers with a versatile toolkit to bring their creative visions to life. One indispensable skill for achieving well-balanced and aesthetically pleasing designs is the ability to distribute objects effectively. This exhaustive guide aims to explore the intricacies of distributing objects in CorelDRAW, catering to both beginners seeking foundational knowledge and experienced designers looking to refine their distribution techniques.
I. Understanding the Concept of Object Distribution:
- Defining Object Distribution: Object distribution involves arranging and spacing design elements in a balanced and orderly manner. This process ensures that objects maintain consistent intervals and alignments, contributing to the overall visual harmony of the design.
- Significance of Object Distribution: Proper object distribution is crucial for achieving a polished and professional look in graphic design. It enhances visual appeal, readability, and overall design coherence, making compositions more engaging and effective.
II. Basic Techniques for Distributing Objects:
- Selecting Multiple Objects: Initiate the distribution process by selecting the objects you want to distribute. This can be done using the Pick tool and clicking on individual objects while holding down the Shift key or by drawing a selection box around the desired elements.
- Accessing the Align and Distribute Docker: CorelDRAW provides a dedicated docker for aligning and distributing objects. Access it by navigating to the “Window” menu and selecting “Dockers,” then choosing “Align and Distribute.”
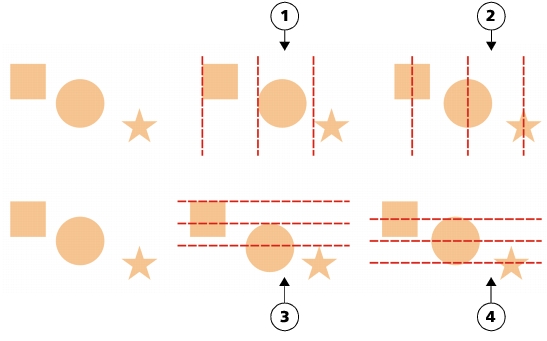
- Distributing Horizontally and Vertically: Use the Align and Distribute docker to distribute objects horizontally or vertically. Options such as “Distribute Center,” “Distribute Top,” “Distribute Bottom,” “Distribute Left,” and “Distribute Right” allow for precise spacing based on the selected reference point.
III. Advanced Distribution Techniques:
- Distributing Evenly: The Align and Distribute docker offers options for distributing objects evenly. Whether spacing objects horizontally or vertically, these tools ensure consistent intervals between each element, creating a balanced and visually appealing design.
- Distributing Along a Path: CorelDRAW enables designers to distribute objects along a path, providing a dynamic way to arrange elements in a curved or custom formation. This technique is valuable for creating intricate designs with flowing compositions.
IV. Distributing Objects Using Object Coordinates:
- Accessing Object Coordinates: For precision distribution, use the property bar or options bar to input specific object coordinates. This method ensures accurate spacing of objects based on X and Y coordinates, allowing for meticulous design control.
- Using the Distribute to Page Option: CorelDRAW provides a “Distribute to Page” option, enabling designers to distribute objects relative to the entire page rather than the selection. This is particularly useful for distributing objects on a larger scale within the document.
V. Troubleshooting and Best Practices:
- Handling Distribution Distortions: In cases where distribution results in distortions, use the Object Manager to check the stacking order of objects. Adjust the order to ensure that the desired objects are distributed without interference from overlapping elements.
- Undo/Redo Functionality: The Undo (Ctrl + Z) and Redo (Ctrl + Y) commands serve as essential tools for troubleshooting distribution issues. If unintended modifications occur during the distribution process, these commands help navigate through the editing history.
VI. Collaboration and Object Distribution:
- Sharing Distribution Specifications: When collaborating on design projects, communicate distribution specifications with team members. Clearly define the distribution parameters, reference points, and any specific design requirements to maintain consistency across the project.
- Version Compatibility: Be mindful of version compatibility when sharing designs. Different versions of CorelDRAW may handle distribution features differently, potentially affecting the accuracy of distributed elements.
VII. Documenting Design Processes:
- Creating Distribution Guides: Document the process of distributing objects for educational or collaborative purposes. Tutorials, design process documents, or annotations within the design file can guide team members or serve as future references.
- Maintaining Design Consistency: Adhere to a standardized approach when distributing objects, ensuring a consistent unit of measurement, reference points, and precision standards across the entire project.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering the art of distributing objects in CorelDRAW is a fundamental skill that significantly contributes to the professionalism and visual coherence of graphic designs. By understanding and implementing the techniques outlined in this guide, designers can achieve precise and harmonious compositions. Embrace the power of object distribution, and let your designs shine with clarity and visual appeal in the dynamic world of graphic design.