Introduction to Installing Drivers in Windows 7
Drivers are software components that facilitate communication between hardware devices and the operating system. Installing the correct drivers ensures that your hardware functions optimally and integrates smoothly with Windows 7. Whether you’re setting up a new device, troubleshooting issues, or upgrading hardware components, knowing how to install drivers is crucial. This guide offers comprehensive instructions on how to install drivers in Windows 7, covering methods such as automatic updates, manual installation via Device Manager, and using manufacturer-provided installation software.
Methods to Install Drivers in Windows 7
Method 1: Automatic Driver Installation via Windows Update
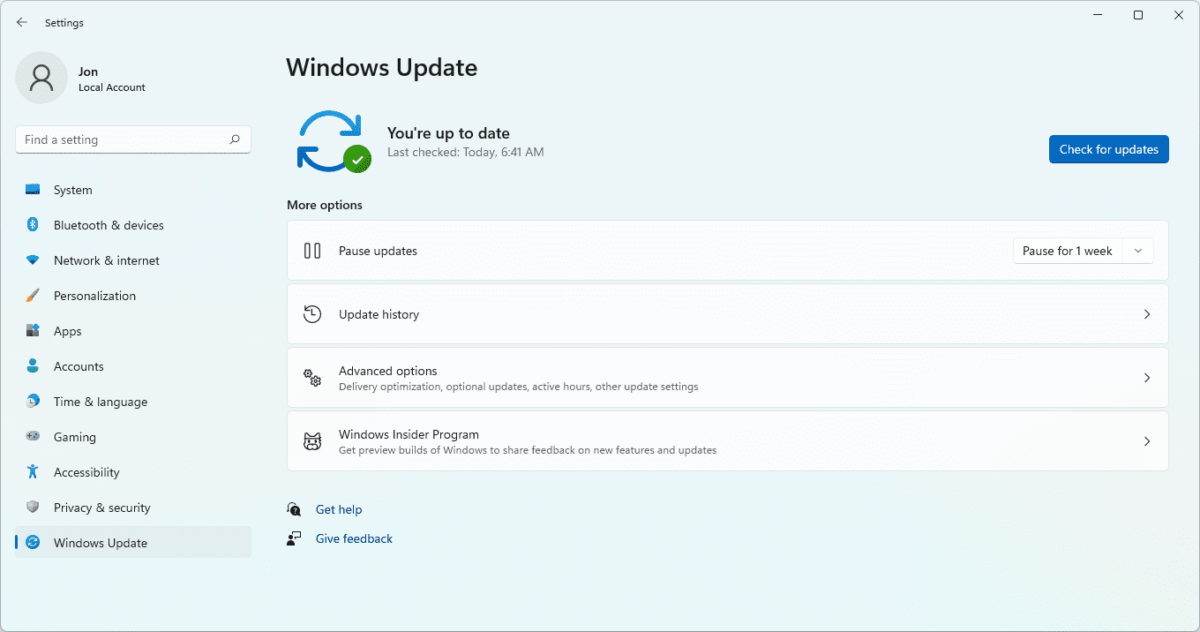
- Open Windows Update:
- Click on the Start button (Windows icon) in the bottom-left corner of the screen and type “Windows Update” in the search box. Select “Windows Update” from the search results.
- Check for Updates:
- Click on “Check for updates” to allow Windows Update to scan your computer for available updates, including driver updates.
- Install Recommended Updates:
- If Windows Update finds driver updates, it will list them under “Optional updates” or “Recommended updates.” Check the box next to the driver update(s) you want to install and click on “Install updates.”
- Restart Your Computer:
- After installing driver updates, restart your computer to apply the changes.
Method 2: Manual Installation via Device Manager
- Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button (Windows icon) and select “Device Manager” from the context menu. Alternatively, press
Win + Xand then select Device Manager.
- Right-click on the Start button (Windows icon) and select “Device Manager” from the context menu. Alternatively, press
- Locate the Device:
- In Device Manager, locate the device category (e.g., Display adapters, Network adapters) that corresponds to the hardware for which you want to install drivers.
- Install the Driver:
- Right-click on the device and select “Update driver.” Choose either “Search automatically for updated driver software” to let Windows search for drivers online, or “Browse my computer for driver software” if you have downloaded the driver installation file.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions:
- If you choose to browse for driver software, navigate to the location where you saved the downloaded driver files, select the .inf file, and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Method 3: Using Manufacturer-Provided Installation Software
- Download Driver Software:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website of your hardware device (e.g., graphics card manufacturer, printer manufacturer) and locate the support or downloads section.
- Select Your Device Model:
- Find and download the latest driver software specific to your device model and Windows 7 operating system version (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Run the Installer:
- Double-click on the downloaded driver installation file (.exe or .msi) to launch the installation wizard.
- Follow Installation Instructions:
- Follow the on-screen prompts to install the driver software. This may include accepting license agreements, selecting installation options, and restarting your computer if prompted.
Additional Tips and Considerations
- Driver Updates:
- Regularly check for driver updates to ensure compatibility, performance enhancements, and bug fixes for your hardware devices.
- Backup Drivers:
- Consider backing up your current drivers using third-party software or built-in Windows tools like System Restore before installing new drivers, especially for critical hardware components.
- Troubleshooting Driver Issues:
- If you encounter issues after installing drivers (e.g., hardware not recognized, performance issues), you can roll back to the previous driver version or uninstall the driver via Device Manager and reinstall it.
- Verify Compatibility:
- Ensure that the driver version you download is compatible with your specific hardware device model and Windows 7 operating system version (32-bit or 64-bit).
Conclusion
Installing drivers in Windows 7 is an essential process for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility of your hardware devices with the operating system. By following the step-by-step instructions provided in this guide using Windows Update, Device Manager, or manufacturer-provided installation software, you can effectively install drivers and maintain the functionality of your computer’s hardware components.
Take advantage of automatic updates via Windows Update or manually install drivers via Device Manager or manufacturer websites to keep your system up-to-date and running smoothly in Windows 7. Regularly updating drivers helps mitigate compatibility issues, enhances performance, and ensures a seamless computing experience.