Named ranges in Excel provide a powerful way to organize and manage data by assigning descriptive names to specific ranges of cells. This allows users to refer to these ranges by name rather than by cell references, making formulas easier to read, understand, and maintain. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about creating and using named ranges in Excel, from basic concepts to advanced techniques and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Using Named Ranges
- Creating Named Ranges
- Practical Examples
- Single Cell Named Ranges
- Contiguous Range Named Ranges
- Non-Contiguous Range Named Ranges
- Advanced Techniques
- Using Named Ranges in Formulas
- Dynamic Named Ranges
- Scope and Visibility of Named Ranges
- Managing Named Ranges
- Editing Named Ranges
- Deleting Named Ranges
- Organizing Named Ranges
- Handling Errors
- Common Errors and Troubleshooting
- Ensuring Data Integrity
- Tips and Tricks
- Using Named Ranges with Tables
- Creating Named Constants
- Naming Conventions
- Real-World Applications
- Financial Modeling
- Data Analysis
- Reporting
- Best Practices
- Choosing Descriptive Names
- Documenting Named Ranges
- Regularly Reviewing Named Ranges
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Named ranges in Excel allow users to assign meaningful names to specific ranges of cells, making it easier to reference and work with data in formulas, charts, and other features. By creating named ranges, users can improve the readability, maintainability, and efficiency of their Excel workbooks.
2. Benefits of Using Named Ranges
- Readability: Named ranges make formulas and functions easier to read and understand by replacing cell references with descriptive names.
- Ease of Use: Users can quickly reference named ranges in formulas, reducing the likelihood of errors and speeding up data entry.
- Flexibility: Named ranges can be used in various Excel features, including charts, conditional formatting, and data validation, enhancing the versatility of Excel workbooks.
- Data Integrity: By using named ranges, users can ensure that formulas and functions always reference the intended cells, even if the layout of the worksheet changes.
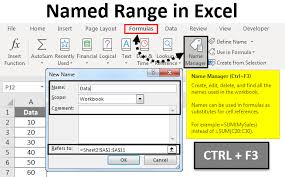
3. Creating Named Ranges
Creating named ranges in Excel is a straightforward process that can be done using the Name Box or the Define Name feature in the Formulas tab.
Using the Name Box:
- Select the range of cells you want to name.
- Click on the Name Box, located to the left of the formula bar.
- Type the desired name for the range and press Enter.
Using the Define Name Feature:
- Select the range of cells you want to name.
- Go to the Formulas tab and click on Define Name.
- Enter the desired name for the range in the Name field and click OK.
4. Practical Examples
Single Cell Named Ranges
To create a named range for a single cell:
- Select the cell.
- Enter a name for the range using either the Name Box or the Define Name feature.
Contiguous Range Named Ranges
To create a named range for a contiguous range of cells:
- Select the range of cells.
- Enter a name for the range using either the Name Box or the Define Name feature.
Non-Contiguous Range Named Ranges
To create a named range for a non-contiguous range of cells:
- Select the first range of cells.
- Hold down the Ctrl key and select additional ranges of cells.
- Enter a name for the range using either the Name Box or the Define Name feature.
5. Advanced Techniques
Using Named Ranges in Formulas
Once named ranges are created, they can be easily referenced in formulas by typing the name instead of the cell reference. For example, instead of typing “=A1+B1”, you can type “=Total” if “Total” is the name of the range containing cells A1 and B1.
Dynamic Named Ranges
Named ranges can be made dynamic by using formulas to define the range. For example, you can use the OFFSET or INDEX functions to define a named range that automatically adjusts its size based on the data in the worksheet.
Scope and Visibility of Named Ranges
Named ranges can have workbook-level or worksheet-level scope, meaning they can be accessed from any worksheet within the workbook or only from the worksheet on which they are defined. Understanding scope is important when working with multiple worksheets or workbooks.
6. Managing Named Ranges
Editing Named Ranges
To edit a named range, go to the Formulas tab, click on Name Manager, select the named range you want to edit, and click Edit. You can then modify the range reference or the name itself.
Deleting Named Ranges
To delete a named range, go to the Formulas tab, click on Name Manager, select the named range you want to delete, and click Delete.
Organizing Named Ranges
To organize named ranges, you can group them into categories or use prefixes/suffixes to indicate their purpose or location within the workbook.
7. Handling Errors
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
- #NAME? Error: This error occurs if the name used in a formula does not match any defined named ranges.
- #REF! Error: This error occurs if a named range refers to cells that have been deleted or are no longer valid.
Ensuring Data Integrity
To ensure data integrity when working with named ranges, regularly review and update named ranges as needed, especially if the layout of the worksheet changes.
8. Tips and Tricks
Using Named Ranges with Tables
Named ranges can be used with Excel tables to create dynamic formulas that automatically adjust as the table size changes.
Creating Named Constants
Named ranges can be used to define constants that are used repeatedly in formulas, making it easier to update values across multiple formulas.
Naming Conventions
Develop a consistent naming convention for named ranges to make them easier to identify and use. For example, use descriptive names that indicate the purpose or contents of the range.
9. Real-World Applications
Financial Modeling
Named ranges can be used to organize financial data and create dynamic financial models that automatically update as new data is entered.
Data Analysis
Named ranges can be used to define data sets for analysis, making it easier to perform calculations and create reports.
Reporting
Named ranges can be used to define ranges of cells for use in charts, pivot tables, and other reporting tools, making it easier to create dynamic reports that update automatically.
10. Best Practices
Choosing Descriptive Names
Use descriptive names for named ranges that accurately reflect the contents or purpose of the range.
Documenting Named Ranges
Document the purpose and usage of named ranges in a worksheet or workbook to provide guidance to other users.
Regularly Reviewing Named Ranges
Regularly review and update named ranges as needed to ensure they remain accurate and up-to-date.
11. Conclusion
Named ranges in Excel provide a powerful way to organize and manage data, making it easier to work with complex worksheets and perform calculations.