Configuring power options in Windows 8 is crucial for optimizing the energy efficiency of your computer and customizing its behavior to suit your preferences and usage patterns. By adjusting power settings, you can control when your computer goes to sleep, when the display turns off, and how much power is consumed by various components. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about configuring power options in Windows 8, from accessing power settings to customizing advanced power plans and managing power-related features effectively.
Understanding Power Options:
Power options in Windows 8 allow you to manage how your computer consumes and conserves energy. By adjusting power settings, you can control aspects such as screen brightness, sleep mode behavior, power plan configurations, and more. Configuring power options not only helps save energy and extend battery life but also allows you to tailor your computer’s performance and behavior to your specific needs and preferences.
Accessing Power Options:
To access power options in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel: Press the Windows key + X to open the Power User menu, then click or tap on “Control Panel.”
- Access Power Options: In the Control Panel, navigate to “System and Security” > “Power Options.” Alternatively, you can search for “Power Options” in the Control Panel search bar or the Start menu.
- Choose Power Plan: In the Power Options window, you’ll see a list of available power plans, such as “Balanced,” “High performance,” and “Power saver.” Click or tap on a power plan to select it and view its settings.
Customizing Power Plans:
Windows 8 allows you to customize power plans to suit your specific needs and preferences. Here’s how to customize power plans:
- Edit Plan Settings: Click or tap on “Change plan settings” next to the selected power plan to customize its settings.
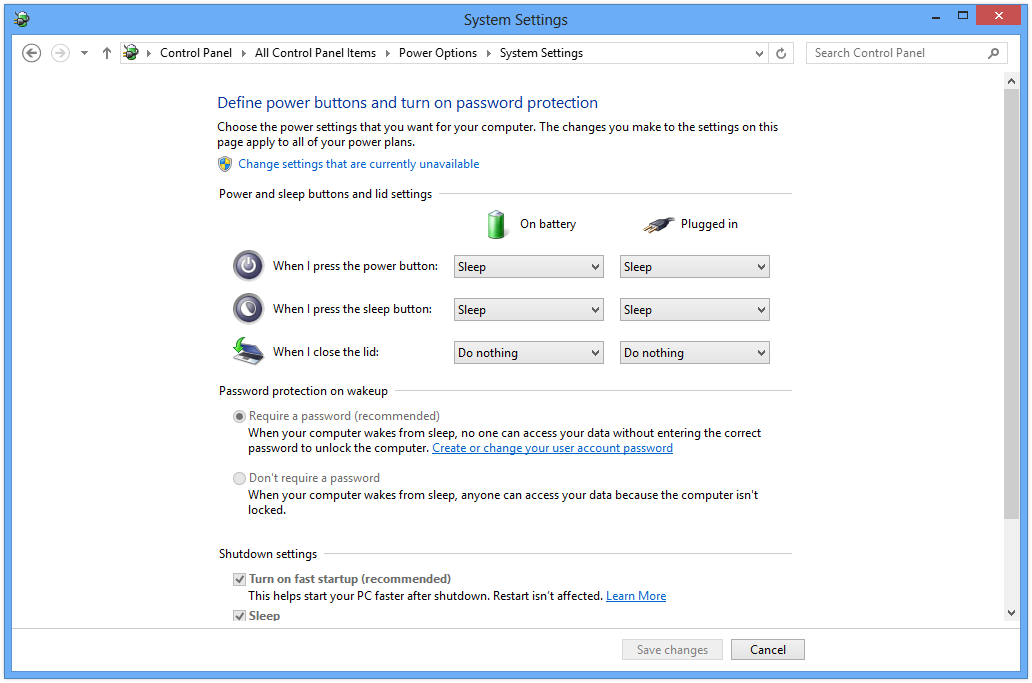
- Adjust Display and Sleep Settings: In the plan settings window, you can adjust settings such as screen brightness, display turn-off time, and sleep mode behavior. Drag the sliders to adjust the desired values or choose from the available options in the drop-down menus.
- Advanced Power Settings: For more advanced settings, click or tap on “Change advanced power settings.” This opens the Power Options dialog box, where you can customize detailed power settings for various components and features, such as processor power management, PCI Express settings, and USB selective suspend.
- Save Changes: Once you’ve customized the power plan settings to your liking, click or tap on “Save changes” to apply the changes and update the power plan.
Creating Custom Power Plans:
In addition to the default power plans provided by Windows 8, you can create custom power plans tailored to your specific usage scenarios. Here’s how to create a custom power plan:
- Access Power Options: Follow the steps outlined earlier to access Power Options in the Control Panel.
- Create a Power Plan: In the Power Options window, click or tap on “Create a power plan” in the left pane.
- Choose Plan Settings: Select one of the existing power plans as a starting point for your custom plan, then click or tap on “Next.”
- Customize Plan Settings: Customize the power plan settings according to your preferences, adjusting parameters such as display brightness, sleep mode behavior, and advanced power settings as needed.
- Name the Plan: Give your custom power plan a descriptive name that reflects its intended usage scenario, then click or tap on “Create” to create the plan.
- Apply Plan: Once the custom power plan is created, it will appear in the list of available power plans. Select the newly created plan to apply its settings.
Managing Power Features:
In addition to configuring power plans, Windows 8 provides various power-related features and settings that you can manage to further optimize energy efficiency and performance. Here are some power features you can manage:
- Battery Saver: If you’re using a laptop or tablet, Windows 8 includes a Battery Saver feature that helps conserve battery life by adjusting system settings and background activity when the battery level is low. You can enable or disable Battery Saver and customize its settings in the Battery settings section of the Settings app.
- Hibernate Mode: Hibernate mode is a power-saving feature that saves the current state of your computer to the hard drive and shuts down the system, allowing you to resume your work later without losing any data. You can enable or disable Hibernate mode and customize its settings in the Power Options dialog box.
- Wake Timers: Windows 8 allows certain programs and system tasks to wake up your computer from sleep or hibernate mode to perform scheduled tasks, such as updates and maintenance. You can manage wake timers and customize their behavior in the Power Options dialog box under Advanced settings.
- USB Selective Suspend: USB Selective Suspend is a power-saving feature that allows Windows to selectively suspend USB devices to conserve power when they’re not in use. You can enable or disable USB Selective Suspend and customize its settings in the Power Options dialog box under Advanced settings.
Troubleshooting Power Issues:
If you encounter issues with power management or experience unexpected behavior related to power options in Windows 8, here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check Power Adapter: If you’re using a laptop or tablet, make sure that the power adapter is connected properly and that the battery is charging correctly.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that device drivers, especially those related to power management and system components, are up to date. Use Device Manager to check for driver updates or visit the manufacturer’s website to download the latest drivers.
- Run Power Troubleshooter: Windows 8 includes a built-in Power troubleshooter that can help diagnose and fix common power-related issues automatically. You can access the Power troubleshooter from the Control Panel or Settings app.
- Check Power Settings: Review your power settings and make sure that they’re configured correctly for your usage scenario. Adjust settings such as sleep mode behavior, display turn-off time, and power plan configurations as needed.
Conclusion:
Configuring power options in Windows 8 is essential for optimizing energy efficiency, extending battery life, and customizing your computer’s behavior to suit your preferences and usage patterns. By accessing power settings, customizing power plans, managing power features, and troubleshooting power-related issues, you can ensure that your computer operates efficiently and effectively while minimizing energy consumption and maximizing performance. Whether you’re using a desktop, laptop, or tablet, Windows 8 provides the tools and resources you need to manage power options effectively and optimize your computing experience.