The journey from CAD model to finished part culminates in the creation of G-code, the language that instructs your CNC machine on how to move the cutting tool and manipulate the workpiece. PowerMill Ultimate empowers you to generate efficient and accurate G-code, transforming your meticulously crafted toolpaths into a set of actionable commands for your machine. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of G-code generation in PowerMill Ultimate, equipping you with the knowledge and techniques to translate your machining vision into reality.
Understanding G-code: The Backbone of CNC Machining
G-code, short for “Graphical code” or “Geometric code,” is a standardized language used to program the movements of CNC machines. Each line of G-code instructs the machine on various parameters, including:
Axis Movements: G-code defines the movement of the cutting tool along the X, Y, Z, and potentially additional rotary axes (A, B, C) for 5-axis machining. The specific G-code commands (G0 for rapid positioning, G1 for linear interpolation, etc.) dictate the type of movement and the target coordinates.
Spindle Speed and Feed Rate: G-code specifies the desired spindle speed (RPM) and feed rate (mm/min or in/min) for the cutting tool during machining operations.
Tool Changes: G-code commands initiate tool changes, instructing the machine to retract the current tool, select a new tool from the tool magazine, and position it at the starting point of the next toolpath.
Coolant Control: G-code can activate and deactivate the coolant system at specific points in the machining process, ensuring optimal chip evacuation and tool lubrication.
Other Auxiliary Functions: G-code can control various auxiliary functions of the CNC machine, such as activating/deactivating the mist collector, turning on/off the work light, or triggering custom machine-specific functions.
By understanding the fundamental elements of G-code, you gain a deeper appreciation for the capabilities of PowerMill Ultimate in generating efficient and precise machine instructions.
The PowerMill G-code Generation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Generating G-code in PowerMill Ultimate involves a streamlined process:
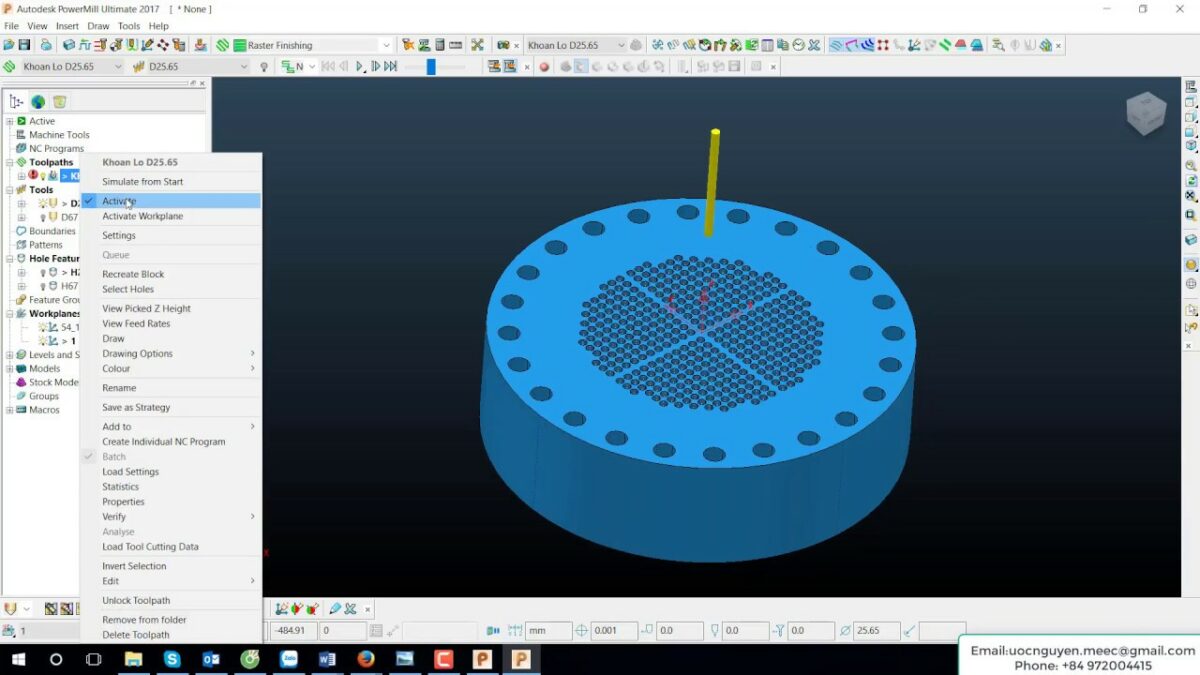
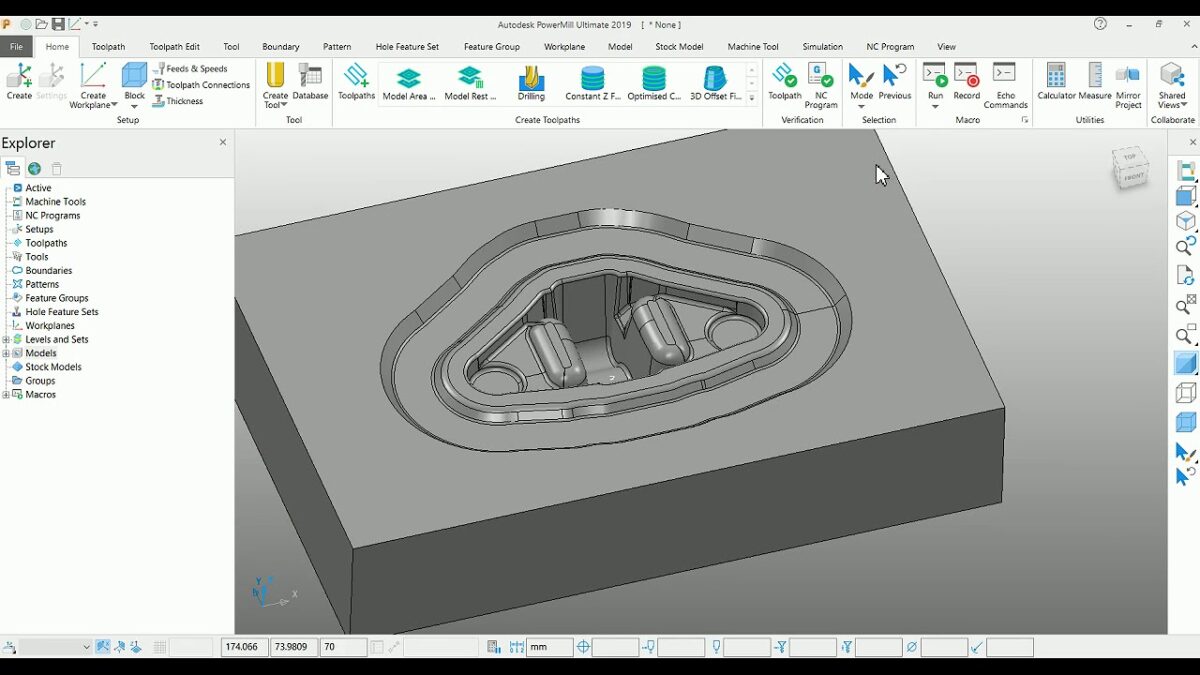
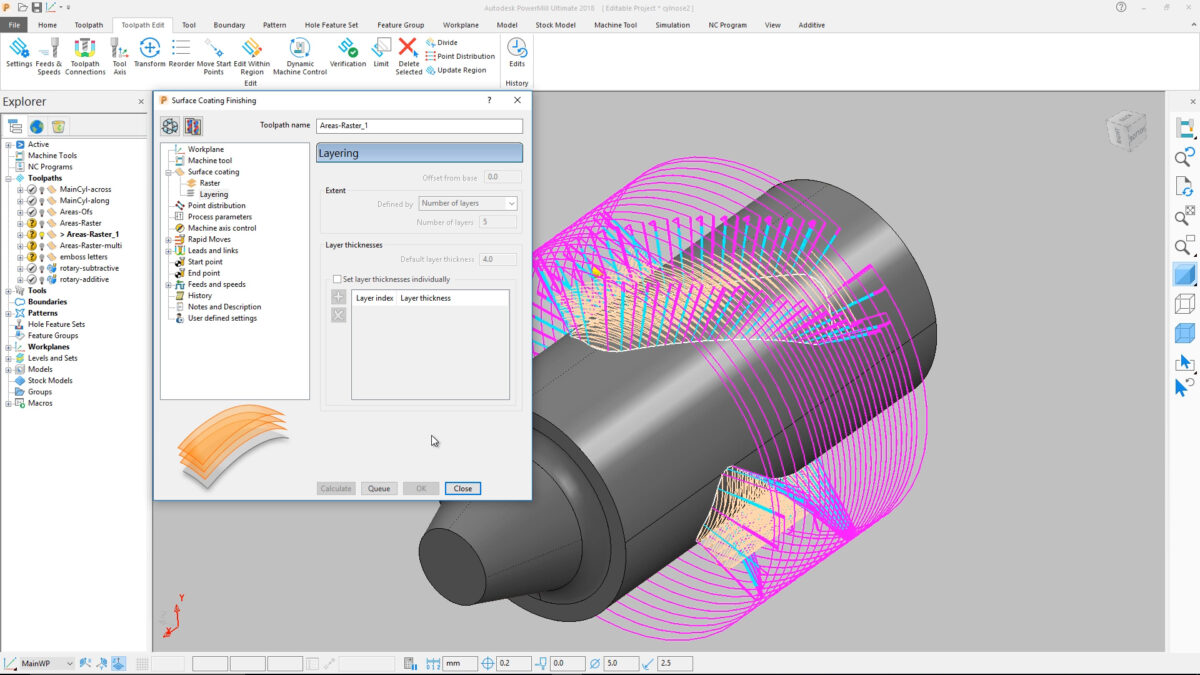
Toolpath Definition: The foundation of G-code generation lies in the creation of accurate and efficient toolpaths within PowerMill. Define the desired machining strategies, tool selection, and cutting parameters for each feature you want to machine.
Postprocessor Selection: A postprocessor acts as a translator between PowerMill’s internal toolpath data and the specific G-code dialect understood by your CNC machine. PowerMill offers a vast library of postprocessors for various CNC machine brands and models. Selecting the appropriate postprocessor ensures compatibility with your machine’s control system.
G-code Verification: PowerMill allows you to preview the generated G-code within the software. This vital step involves simulating the toolpath motions and identifying any potential errors or collisions before sending the G-code to the machine.
G-code Output: Once verification is complete and any necessary adjustments are made, PowerMill allows you to output the G-code as a text file. This file can then be transferred to your CNC machine’s control system for execution.
Optimizing Your G-code Generation: Considerations for Efficiency and Reliability
Here are some key considerations for optimizing G-code generation in PowerMill Ultimate:
Postprocessor Configuration: Ensure the selected postprocessor is accurately configured for your specific CNC machine model and control system. This includes defining parameters like axis units (millimeters or inches), coolant control codes, and tool change commands specific to your machine.
Toolpath Smoothing: PowerMill offers functionalities for smoothing toolpaths, minimizing rapid changes in tool direction. This can result in smoother machine movements and potentially extend tool life.
G-code Comments: Adding clear and concise comments within the generated G-code can enhance readability and understanding for the machine operator. This can be particularly beneficial for complex machining operations or when working with multiple G-code files.
Safety Considerations: Always double-check your G-code for potential safety hazards before transferring it to the CNC machine. Verify that all toolpaths and machine movements are within the safe working area of your machine and workpiece.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that the G-code generated by PowerMill Ultimate is not only functional but also optimized for efficient and reliable machining operations.