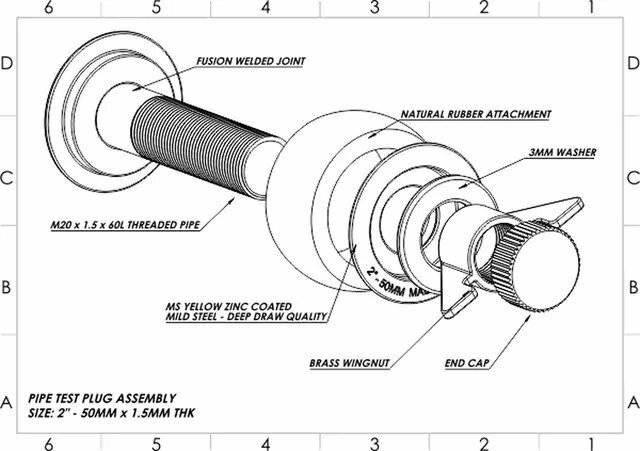
Introduction:
General Assembly Drawings serve as vital documents in the field of engineering and design, providing a comprehensive representation of how various components come together to form a complete product or structure. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of creating detailed General Assembly Drawings in AutoCAD. Covering essential techniques, industry-specific applications, and best practices, this guide aims to equip designers and engineers with the skills needed to produce accurate and informative assembly documentation.
Section 1: Understanding the Significance of General Assembly Drawings
1.1 Overview of General Assembly Drawings: Gain a clear understanding of the purpose and importance of General Assembly Drawings. Explore how these drawings serve as a bridge between individual components and the final assembled product, providing valuable information for manufacturing, construction, and maintenance.
1.2 Types of Assemblies: Delve into the different types of assemblies represented in General Assembly Drawings. Explore mechanical assemblies, architectural structures, electronic assemblies, and more. Each type presents unique challenges and considerations in the assembly drawing process.
Section 2: Setting Up the AutoCAD Environment for Assembly Drawings
2.1 Choosing the Right AutoCAD Template: Start by selecting the appropriate AutoCAD template for assembly drawings. Learn how templates streamline the drawing process by providing predefined layers, linetypes, and settings tailored to assembly documentation.
2.2 Configuring Units and Drawing Limits: Ensure precision in your assembly drawings by configuring units and drawing limits. Explore the implications of unit settings on accuracy, and establish appropriate drawing limits based on the scale and complexity of the assembly.
Section 3: Creating Base Views and Outlines
3.1 Placing Base Views: Master the art of placing base views in AutoCAD. Learn how to generate primary orthographic projections that serve as the foundation for the assembly drawing, providing clear and detailed representations of each component.
3.2 Creating Exploded Views: Explore the creation of exploded views for assemblies with intricate components. Understand how to strategically disassemble parts to illustrate their relationships and positions within the overall structure.
Section 4: Inserting Standard Components and Assemblies
4.1 Utilizing Standard Blocks: Familiarize yourself with standard blocks for commonly used components. Learn how to insert predefined blocks for bolts, nuts, washers, and other standard elements, streamlining the drawing process and ensuring consistency.
4.2 Representing Standard Assemblies: Delve into the representation of standard assemblies in AutoCAD. Understand how to insert pre-modeled assemblies, such as gears, pulleys, or electronic components, into the drawing to save time and maintain accuracy.
Section 5: Detailing Individual Components
5.1 Creating Section Views: Master the creation of section views in AutoCAD for detailed components. Explore how section views reveal internal features, dimensions, and relationships within individual parts, enhancing the clarity of your assembly documentation.
5.2 Adding Dimensions and Annotations: Explore the addition of dimensions and annotations to individual components. Learn how to convey critical information such as measurements, materials, and specifications, ensuring clarity and precision in your assembly drawings.
Section 6: Bill of Materials (BOM) and Parts Lists
6.1 Generating a Bill of Materials: Delve into the generation of a Bill of Materials (BOM) for assembly drawings. Learn how to extract information about the types, quantities, and specifications of components, facilitating material procurement and construction planning.
6.2 Parts Lists and Balloons: Explore the creation of parts lists and balloons in AutoCAD. Understand how to label and identify each component within the assembly, providing a clear reference for manufacturing, assembly, and maintenance.
Section 7: Representing Motion and Interactions
7.1 Motion Lines and Arrows: Learn how to represent motion and interactions within the assembly drawing. Explore the use of motion lines and arrows to illustrate the movement or function of specific components, enhancing the understanding of the assembly process.
7.2 Exploded View Animations: Delve into advanced techniques such as creating exploded view animations. Understand how to use AutoCAD or third-party software to generate dynamic visualizations that showcase the assembly process in a step-by-step manner.
Section 8: Customizing Assembly Drawings for Specific Industries
8.1 Mechanical Assemblies: Explore techniques specific to mechanical assemblies. Learn how to represent gears, linkages, and moving parts with precision, considering factors such as clearances, tolerances, and material specifications.
8.2 Architectural and Structural Assemblies: Delve into the customization of assembly drawings for architectural and structural applications. Understand how to represent components such as beams, columns, and connections, providing detailed information for construction and design coordination.
8.3 Electrical and Electronic Assemblies: Explore the representation of electrical and electronic assemblies. Learn how to illustrate the interconnection of components, specify wiring details, and provide information on electrical circuits within the assembly drawing.
Section 9: Advanced Techniques for Large and Complex Assemblies
9.1 Sectional Assembly Views: Master the creation of sectional assembly views for large and complex assemblies. Learn how to strategically cut through the assembly to reveal internal details and enhance the understanding of intricate structures.
9.2 Representing Interference and Clearance: Explore techniques for representing interference and clearance within assemblies. Learn how to use shading, hatch patterns, or color coding to highlight areas of potential conflict or identify spaces for clearances.
Section 10: Annotation and Documentation
10.1 Adding Assembly-Level Dimensions: Master the art of adding assembly-level dimensions. Explore how to provide overall dimensions that encompass the entire assembly, facilitating a holistic understanding of size and scale.
10.2 Detailing and Callouts: Delve into the detailing of specific areas within the assembly. Learn how to use callouts and detailed views to highlight critical features, ensuring that intricate components are accurately represented and understood.
Section 11: Collaborative Workflows and Data Exchange
11.1 Collaborating with Other Disciplines: Explore collaborative workflows with other disciplines in AutoCAD. Understand how assembly drawings integrate with mechanical, architectural, electrical, and plumbing disciplines, facilitating coordination and holistic project development.
11.2 Data Exchange with Other Software: Delve into data exchange between AutoCAD and other software platforms. Understand the importance of interoperability in collaborative projects and explore techniques for importing/exporting data to enhance workflow efficiency.
Section 12: Challenges and Troubleshooting
12.1 Common Challenges in Assembly Drawings: Address common challenges encountered in assembly drawings. From managing complex structures to ensuring accurate representation of interactions, gain insights into effective problem-solving strategies for creating reliable assembly documentation.
12.2 Troubleshooting Tips: Explore troubleshooting tips for resolving issues related to assembly drawings in AutoCAD. From optimizing performance to addressing conflicts with dimensions, understand how to maintain precision and stability in your design process.
Section 13: Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
13.1 Digital Twins and Simulation: Delve into the potential impact of digital twins and simulation in assembly drawings. Explore how digital representations and simulation tools may enhance the understanding of assembly behavior and performance.
13.2 Augmented Reality (AR) for Assembly Visualization: Explore the integration of augmented reality (AR) with assembly drawings in AutoCAD. Learn how AR technologies enhance the immersive experience of interacting with and evaluating assembly designs in real-world contexts.
Conclusion:
As we conclude this exhaustive exploration of creating detailed General Assembly Drawings in AutoCAD, it is evident that mastering the art of assembly documentation requires a combination of technical skills, attention to detail, and an understanding of industry-specific requirements. Whether you are a mechanical engineer designing machinery, an architect planning a complex structure, or an electrical engineer orchestrating intricate circuits, AutoCAD’s capabilities empower you to produce comprehensive and informative assembly drawings. Embrace the versatility, efficiency, and customization that AutoCAD offers in assembly documentation, and witness how this transformative skill elevates your designs from components to fully realized products or structures. With continuous practice, exploration, and innovation, you will navigate the intricate landscape of assembly drawings with confidence, producing documentation that stands as a testament to the power of AutoCAD in the dynamic world of CAD.