In the realm of document design, visual elements play a crucial role in enhancing the aesthetic appeal, professionalism, and security of content. Watermarks, in particular, serve as versatile tools for adding branding, confidentiality statements, or decorative motifs to documents. Whether you’re creating reports, proposals, or presentations, a well-designed watermark can elevate the visual impact and convey important information to your audience. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of creating watermarks in Microsoft Word, empowering you to enhance your document’s visual appeal and functionality with precision and ease.
Understanding the Significance of Watermarks:
Before delving into the practical aspects of creating watermarks, it’s crucial to grasp the significance of these visual elements in document design. Watermarks serve multiple purposes, including:
- Branding and identification: Watermarks allow organizations to add their logo, name, or slogan to documents, reinforcing brand recognition and identity.
- Document security: Watermarks can include confidentiality statements, copyright notices, or other security features to deter unauthorized copying or distribution of sensitive documents.
- Visual enhancement: Watermarks add visual interest and professionalism to documents, enhancing their overall appearance and appeal.
By incorporating watermarks into your document design strategy, you can create documents that are not only visually appealing but also informative, secure, and reflective of your organization’s identity and values.
Basic Watermark Creation:
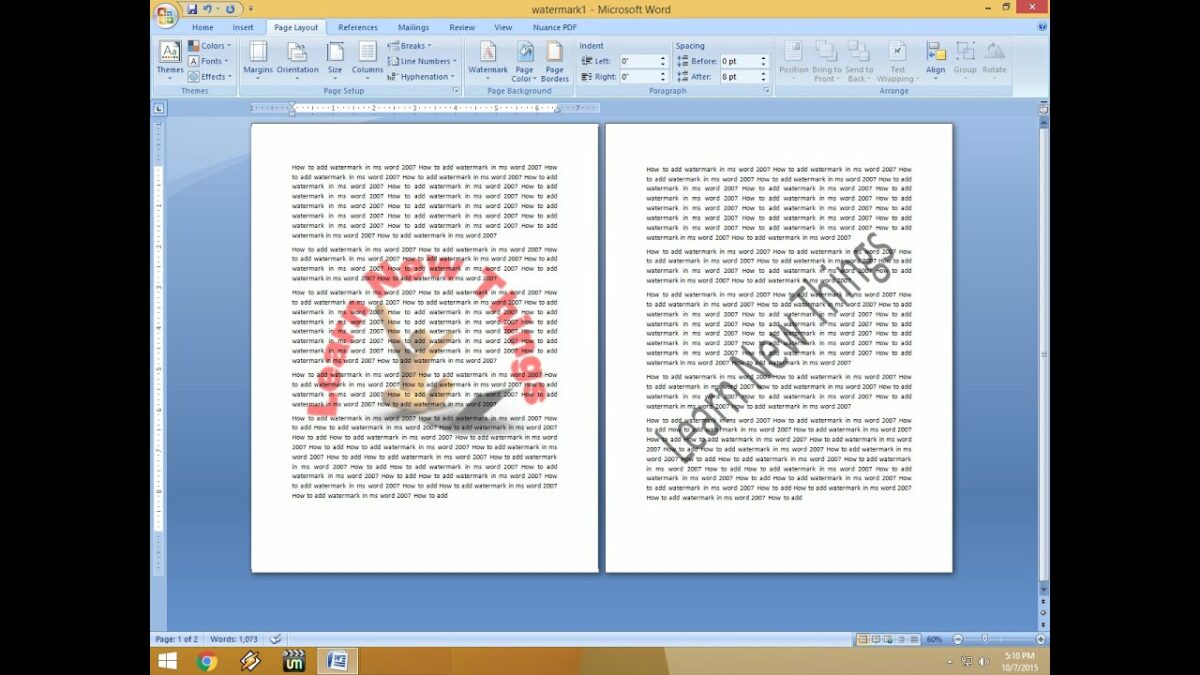
Creating a watermark in Microsoft Word is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using built-in tools and features. Here’s how to do it:
- Access Watermark Options:
- Open Microsoft Word and navigate to the “Design” tab located in the top menu bar.
- In the “Page Background” group, you’ll find the “Watermark” button. Click on this button to access watermark options.
- Choose a Built-in Watermark:
- In the watermark options menu, you’ll see a gallery of built-in watermark designs, including text-based and image-based options.
- Browse through the available designs and choose the one that best suits your document’s style and purpose. Click on the desired watermark to apply it to your document.
- Customize Watermark Text (Optional):
- If you selected a text-based watermark, you can customize the text, font, size, color, and orientation to align with your document’s branding and requirements.
- Double-click on the watermark to edit the text directly, or right-click on it and choose “Edit Watermark” from the context menu to access formatting options.
- Adjust Watermark Transparency (Optional):
- To adjust the transparency of the watermark and make it more subtle or prominent, you can modify the transparency settings.
- Right-click on the watermark, choose “Format Watermark” from the context menu, and adjust the transparency slider to the desired level.
Advanced Watermark Customization:
While basic watermark creation suffices for most scenarios, Microsoft Word offers advanced features and customization options to further enhance the appearance and functionality of watermarks. Here are some additional features you may explore:
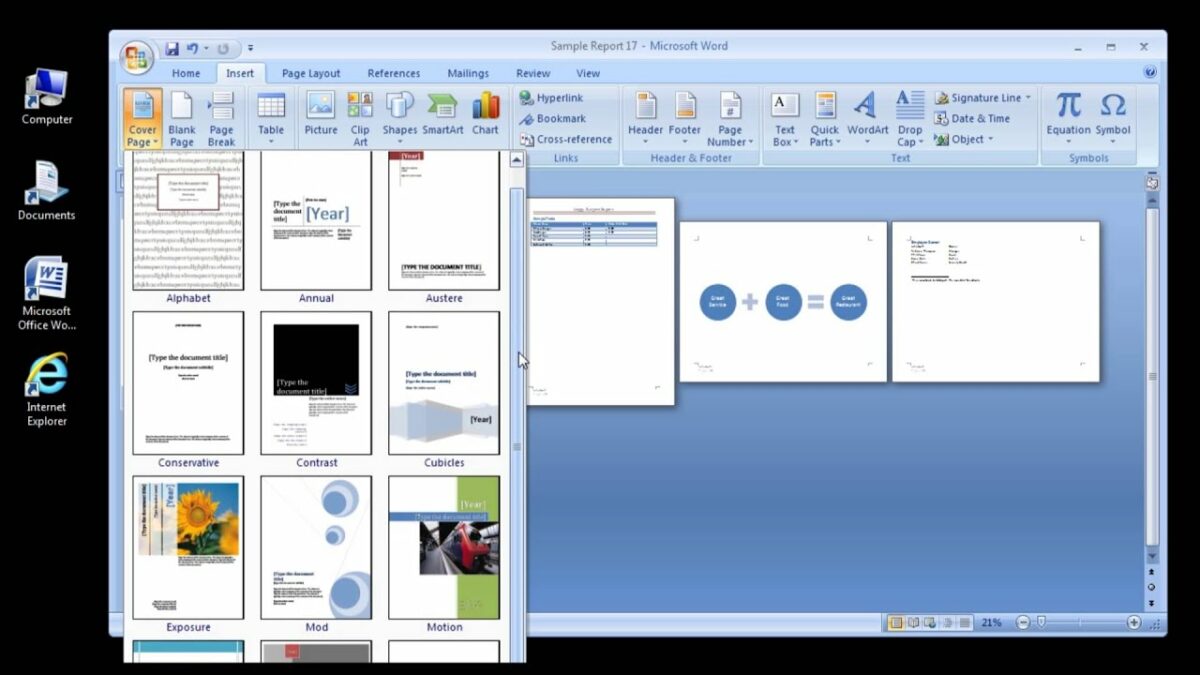
- Create Custom Watermark:
- If the built-in watermark designs don’t meet your requirements, you can create a custom watermark from scratch using text boxes, shapes, images, and other design elements.
- Arrange and format the elements to create a unique and visually appealing watermark that reflects your organization’s branding and messaging.
- Apply Watermark to Specific Pages:
- Word allows users to apply watermarks selectively to specific pages or sections within a document. This feature is particularly useful for adding confidential or draft watermarks to certain pages while leaving others unaffected.
- Navigate to the “Design” tab, click on “Watermark,” and choose “Custom Watermark.” In the dialog box, select the “Apply to” dropdown menu and choose the desired option.
- Save Watermark as Template:
- Once you’ve created a custom watermark or modified an existing one, you can save it as a template for future use.
- Right-click on the watermark, choose “Save as Picture” from the context menu, and save the image file in a location where you can easily access it for future documents.
Best Practices for Watermark Usage:
While watermarks offer versatility and visual enhancement in document design, it’s essential to use them judiciously and in accordance with best practices. Here are some tips to consider:
- Keep it Subtle:
- Avoid using overly distracting or intrusive watermarks that detract from the readability and professionalism of the document. Keep the watermark subtle and unobtrusive while still conveying the desired message or branding.
- Ensure Legibility:
- If using a text-based watermark, ensure that the text is legible and easy to read against the background of the document. Choose a font, size, and color that provide sufficient contrast and visibility.
- Maintain Branding Consistency:
- Ensure that the watermark aligns with your organization’s branding guidelines in terms of colors, fonts, logo placement, and overall aesthetic. Consistent branding enhances recognition and reinforces brand identity.
- Test Across Devices:
- Before finalizing your document, test the appearance and visibility of the watermark across different devices, screen resolutions, and printing settings to ensure that it renders correctly and maintains its visual integrity.
Conclusion:
Creating a watermark in Microsoft Word is a fundamental skill for enhancing document visual appeal, security, and branding. By mastering the basic creation process, exploring advanced customization options, and adhering to best practices for watermark usage, you can create documents that are not only visually appealing but also informative, secure, and reflective of your organization’s identity and values. Whether you’re creating reports, presentations, or marketing materials, a well-designed watermark adds professionalism, credibility, and visual interest to your documents, making them more memorable and impactful. So, the next time you embark on a document creation journey in Word, remember to leverage the power of watermarks to enhance your document’s visual appeal and functionality, and make a lasting impression on your audience.