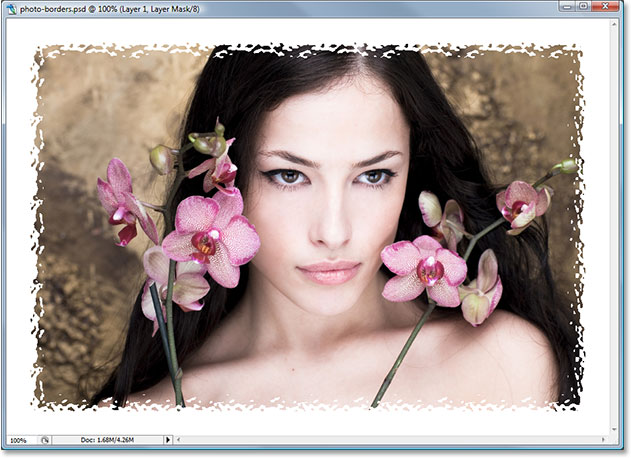
Introduction:
In the realm of digital design and photography, the framing of an image plays a crucial role in enhancing its visual impact. Creating photo borders in Photoshop is an artful technique that goes beyond traditional framing, allowing for the infusion of creativity and personality into your compositions. This extensive guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of crafting intricate photo borders using masks and filters in Photoshop. From selecting the right image to applying advanced masking techniques, this tutorial aims to empower you with the skills to elevate your photo borders to a level of artistic excellence.
Section 1: Choosing the Right Image
Step 1: Selecting a Compelling Image:
Begin by choosing a photograph that captures attention and aligns with your creative vision for the photo border. Consider images with distinct subjects, vibrant colors, or interesting compositions that can serve as a focal point within the border.
Step 2: Assessing Composition:
Pay close attention to the composition of the selected image. Elements like leading lines, symmetry, or a well-defined subject can enhance the effectiveness of your photo border. A thoughtful composition ensures that the border complements and enhances the overall visual narrative.
Section 2: Importing and Organizing Images
Step 1: Transferring Images to Photoshop:
Transfer the selected image to your computer and organize it in a dedicated folder. This organizational step ensures a smooth workflow and easy access to the image during the photo border creation process.
Step 2: Opening Images in Photoshop:
Launch Adobe Photoshop and open the chosen image within the workspace. Use the “File” menu and select “Open” to load the image, preparing it for the photo border design.
Section 3: Basic Adjustments in Adobe Camera Raw
Step 1: Accessing Adobe Camera Raw:
Before delving into photo border creation, make basic adjustments using Adobe Camera Raw. This step involves refining exposure, contrast, and color balance to achieve an optimal starting point for your photo border.
Step 2: Fine-Tuning Highlights and Shadows:
Use the sliders in Adobe Camera Raw to fine-tune highlights and shadows. Balancing these elements ensures that your photo border will complement the overall tone and mood of the image.
Section 4: Initial Image Masking
Step 1: Creating a Duplicate Layer:
To begin the photo border creation, create a duplicate layer of your image. This duplication allows for non-destructive editing, preserving the original image beneath the adjustments.
Step 2: Applying a Layer Mask:
Add a layer mask to the duplicated layer. This mask will be the foundation for shaping the photo border. Utilize the “Brush” tool to selectively reveal or hide parts of the image, defining the boundaries of your border.
Section 5: Introducing Filter Effects
Step 1: Choosing a Filter:
Experiment with various filters to add a distinct visual effect to your photo border. Filters such as Gaussian Blur, Oil Paint, or Brush Strokes can introduce unique textures and atmospheres to enhance the artistic quality of the border.
Step 2: Adjusting Filter Settings:
Fine-tune the filter settings to achieve the desired effect. Control parameters like intensity, size, or complexity to tailor the filter to complement the theme and mood of your photo border.
Section 6: Layer Styles for Dimension
Step 1: Adding Layer Styles:
Enhance the three-dimensional quality of your photo border by applying layer styles. Use effects like Inner Shadow, Bevel and Emboss, or Stroke to add depth and definition to the border’s edges.
Step 2: Customizing Layer Style Settings:
Customize the settings of layer styles to align with the aesthetics of your photo border. Adjust parameters such as opacity, size, or color to achieve a harmonious integration of layer styles with the overall composition.
Section 7: Advanced Masking Techniques
Step 1: Utilizing Advanced Brushes:
For intricate photo borders, employ advanced brushes to refine the layer mask. Brushes with unique textures or patterns can add intricate details, contributing to the complexity and artistry of the border.
Step 2: Experimenting with Brush Opacity and Flow:
Fine-tune the opacity and flow settings of your brushes for nuanced masking. This step allows for precise control over the gradual reveal or concealment of image elements within the photo border.
Section 8: Incorporating Texture Layers
Step 1: Adding Texture Layers:
Elevate the tactile quality of your photo border by incorporating texture layers. Overlay textures such as paper, fabric, or grunge patterns to infuse additional visual interest and depth.
Step 2: Blending Texture Layers:
Experiment with blending modes and opacity settings to seamlessly integrate texture layers with the photo border. This step ensures that the texture enhances the overall aesthetic without overpowering the image.
Section 9: Creative Overlays for Artistry
Step 1: Introducing Creative Overlays:
Explore the addition of creative overlays to impart a distinct atmosphere to your photo border. Overlays like light leaks, bokeh, or abstract patterns can introduce an artistic flair that enhances the overall impact.
Step 2: Adjusting Overlay Blending Modes:
Fine-tune the blending modes of creative overlays to achieve a harmonious blend with the photo border. Experiment with blending modes such as Screen or Overlay to ensure a seamless integration.
Section 10: Color Grading and Toning
Step 1: Selective Color Adjustments:
Refine the color palette of your photo border through selective color adjustments. Use adjustment layers like Color Balance or Hue/Saturation to tailor the color tones to match the desired mood.
Step 2: Introducing Gradient Maps:
Experiment with gradient maps to add depth and dimension to the color grading. Gradient maps allow for creative control over color transitions within the photo border, contributing to a cohesive visual narrative.
Section 11: Final Touches and Global Adjustments
Step 1: Evaluating Overall Composition:
Step back and assess the overall composition of your photo border. Ensure that the added elements, filters, and adjustments contribute to a unified and visually appealing design.
Step 2: Global Adjustments for Cohesion:
Make any final global adjustments to overall color balance, contrast, or saturation. This step ensures that the photo border integrates seamlessly with the broader color scheme and aesthetics of the image.
Section 12: Saving and Exporting
Step 1: Save Your Artwork:
Once satisfied with your photo border creation, save your work in a high-quality format such as PSD. This preserves layers and allows for future edits or refinements.
Step 2: Exporting for Different Platforms:
When ready to share your photo border masterpiece, export it in suitable formats for various platforms. Consider the intended use, whether for print, web, or social media, to ensure the exported file retains the quality and impact of your artistic creation.
Section 13: Troubleshooting Common Challenges
Challenge 1: Uneven Masking:
Address uneven masking by revisiting the layer mask with advanced brushes. Ensure that the masking is consistent and aligns with the intended design of the photo border.
Challenge 2: Overwhelming Filters:
If filters overpower the image, dial back the intensity or complexity settings. Adjust the filter parameters to achieve a balance where the filter enhances without overshadowing the photo border.
Section 14: Showcasing Inspirational Examples
Example 1: Vintage Elegance Border:
Explore a photo border infused with vintage charm, featuring subtle filters, texture layers, and intricate masking for an elegant and timeless aesthetic.
Example 2: Contemporary Abstract Border:
Witness a modern and abstract photo border created through bold filters, creative overlays, and experimental color grading. This example showcases the versatility of photo border design in contemporary digital art.
Section 15: Advancing Skills in Photo Border Design
Step 1: Experimenting with Styles:
Expand your photo border design skills by experimenting with different styles. Explore minimalistic borders, ornate frames, or thematic designs to diversify your creative repertoire.
Step 2: Pushing the Boundaries of Creativity:
Challenge yourself to push the boundaries of creativity within photo border design. Integrate unconventional elements, experiment with asymmetry, or combine various techniques to create borders that defy traditional norms.
Conclusion:
Creating photo borders in Photoshop with masks and filters is a dynamic fusion of technical skill and artistic intuition. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the tools and techniques needed to transform your images into visually captivating compositions. As you embark on your journey of photo border design, let your creativity flourish and infuse your personal style into each border you craft. Embrace the artistry of photo borders – let them become a testament to your mastery of design, attention to detail, and the seamless marriage of technology and creativity in the digital canvas of Photoshop.