Introduction:
In the fast-paced world of audio production, efficiency, flexibility, and mobility are paramount. Avid’s Pro Tools Control app offers a powerful solution, allowing users to control their Pro Tools sessions from the convenience of their iOS or Android device. Whether you’re in the studio, on the go, or collaborating with remote collaborators, the Pro Tools Control app empowers you to stay connected and in control of your projects. In this exhaustive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of the Pro Tools Control app, from setup and configuration to advanced features and practical applications, helping you unlock its full potential for music production, sound design, and audio post-production.
Understanding the Pro Tools Control App:
Before delving into the specifics of using the Pro Tools Control app, let’s establish a foundational understanding of its core concepts and components:
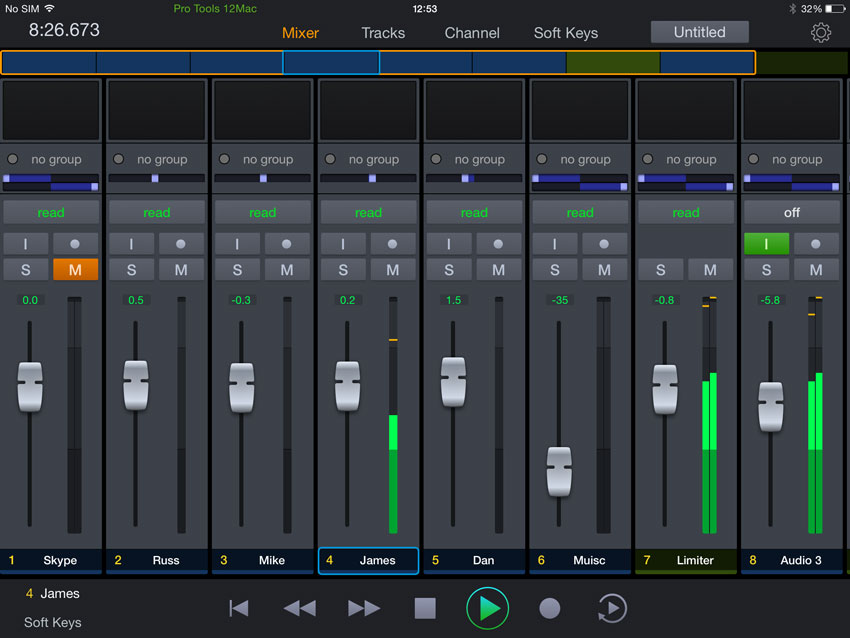
- Remote Control: The Pro Tools Control app serves as a remote control surface for Pro Tools, allowing users to control various aspects of their sessions wirelessly from their mobile devices. With the Pro Tools Control app, users can access essential controls, parameters, and functions directly from their iOS or Android device, enhancing workflow and productivity.
- Compatibility: The Pro Tools Control app is compatible with Pro Tools | S6, Pro Tools | S3, and Artist Series control surfaces, providing seamless integration and control over Pro Tools sessions. Additionally, the app supports EuControl, Avid’s protocol for connecting control surfaces and applications, ensuring reliable and responsive communication between the app and Pro Tools.
- Features: The Pro Tools Control app offers a wide range of features and functionalities, including track control, channel control, automation control, transport control, navigation control, and more. Users can access faders, knobs, buttons, and touch-sensitive displays to interact with their Pro Tools sessions intuitively and efficiently.
- Customization: The Pro Tools Control app allows users to customize the layout, functions, and settings according to their preferences and workflow. Users can create custom layouts, assign functions to buttons and knobs, and save presets for quick access, ensuring a tailored and personalized experience.
Getting Started with the Pro Tools Control App:
Now that we have a foundational understanding of the Pro Tools Control app, let’s explore the step-by-step process of using the app in your workflow:
- Downloading and Installing the App:
- Download and install the Pro Tools Control app from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android) on your mobile device. Ensure that your device is running the latest version of the operating system and meets the minimum requirements for compatibility with the app.
- Connecting to Pro Tools:
- Connect your mobile device to the same network as your Pro Tools workstation. Launch the Pro Tools Control app and select your Pro Tools workstation from the list of available devices. Follow the on-screen instructions to establish a connection between the app and Pro Tools.
- Navigating the Interface:
- Familiarize yourself with the interface and layout of the Pro Tools Control app. Explore the various screens, tabs, and controls available, including track view, channel view, automation view, transport view, and more. Swipe, tap, and pinch-to-zoom to navigate through different sections of your Pro Tools session.
- Controlling Your Session:
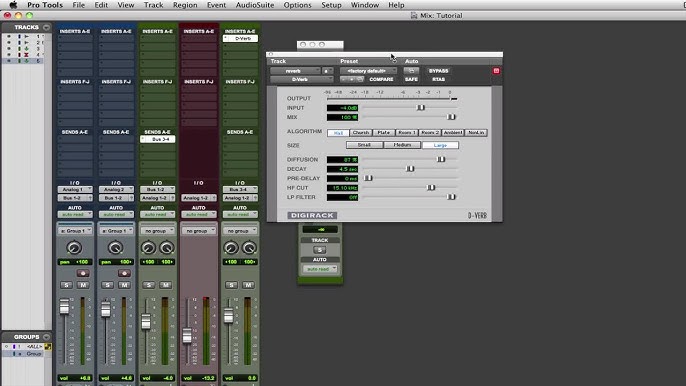
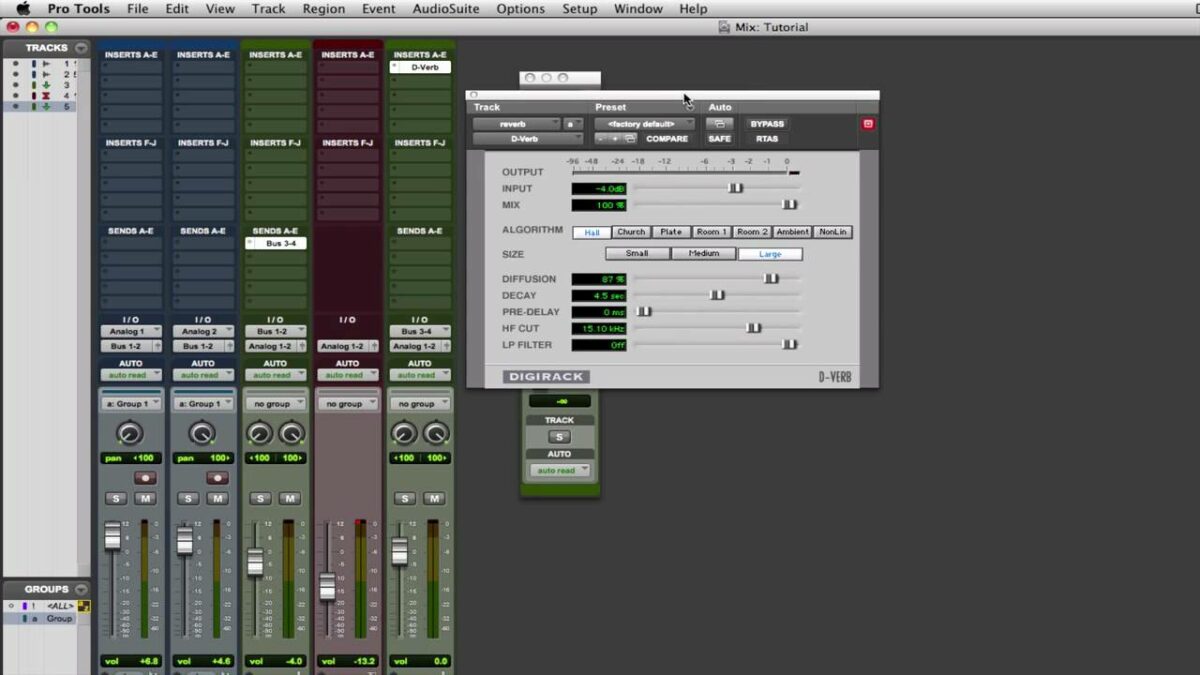
- Use the Pro Tools Control app to control various aspects of your session, including track levels, panning, solo, mute, record enable, automation modes, and transport controls. Tap on faders, knobs, buttons, and touch-sensitive displays to make adjustments and changes in real-time, enhancing workflow and creativity.
Advanced Features and Practical Applications:
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, consider exploring some advanced features and practical applications of the Pro Tools Control app:
- Custom Layouts: Create custom layouts in the Pro Tools Control app to tailor the interface and controls to your specific needs and preferences. Arrange faders, knobs, buttons, and displays according to your workflow, grouping related controls together for quick access and efficiency.
- Multi-Touch Gestures: Take advantage of multi-touch gestures, such as two-finger swipes and pinch-to-zoom, to navigate and interact with your Pro Tools session more efficiently. Use multi-touch gestures to zoom in and out on waveforms, scroll through tracks and channels, and access additional functions and parameters.
- Remote Collaboration: Use the Pro Tools Control app for remote collaboration and communication with collaborators, clients, and team members. Share control of your Pro Tools session with remote users, allowing them to make adjustments and provide feedback in real-time, regardless of their location.
- Mobile Mixing: Take your mixing sessions on the go with the Pro Tools Control app, allowing you to mix and edit your Pro Tools sessions from anywhere with an internet connection. Whether you’re traveling, commuting, or working from a different location, the Pro Tools Control app keeps you connected and productive.
Conclusion:
The Pro Tools Control app offers a versatile and powerful solution for controlling Pro Tools sessions remotely from your mobile device. By mastering the art of using the Pro Tools Control app, users can enhance efficiency, flexibility, and mobility in their audio production workflow.
Whether you’re in the studio, on the go, or collaborating with remote collaborators, the Pro Tools Control app empowers you to stay connected and in control of your projects. So, download the app, connect to Pro Tools, and let the boundless possibilities of remote control in Pro Tools elevate your creative journey to new heights.