Introduction: MATLAB is a powerful programming language and computing environment widely used in engineering, science, and academia for data analysis, numerical computation, and algorithm development. One of the fundamental skills in MATLAB is creating and running scripts, which are files containing a sequence of MATLAB commands that can be executed together. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of how to create and run MATLAB scripts, offering step-by-step insights and expert tips to empower users to harness the full potential of MATLAB for their projects and tasks.
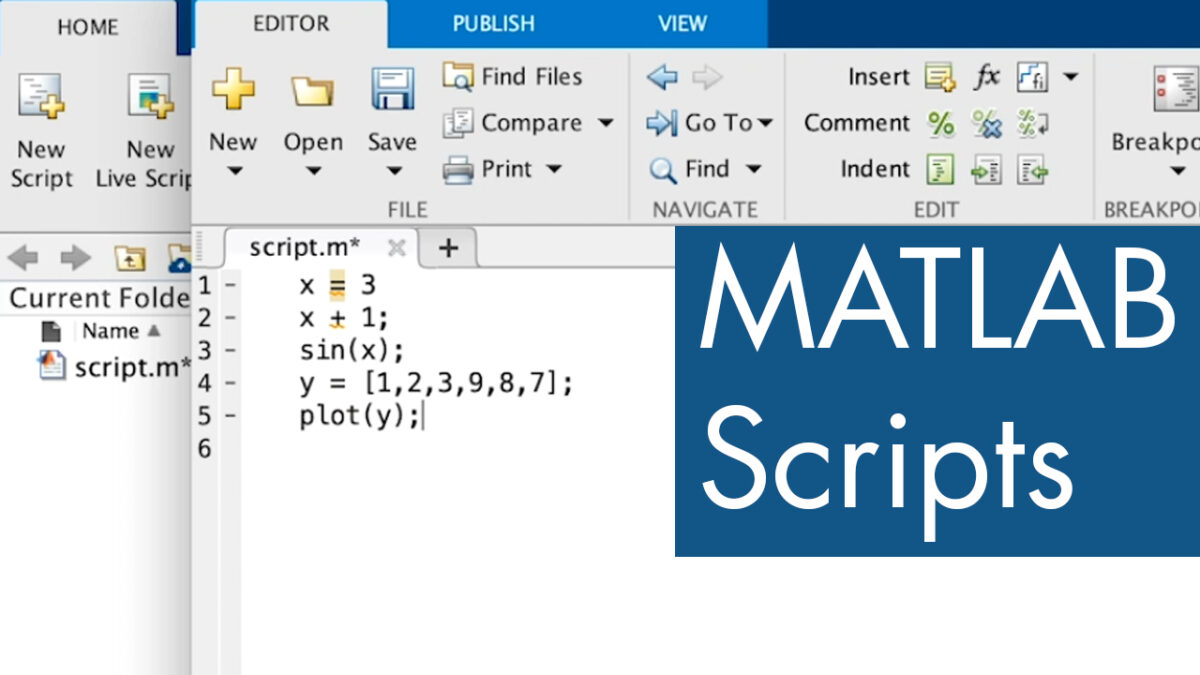
Understanding MATLAB Scripts: A MATLAB script is a plain text file containing a series of MATLAB commands and statements that are executed sequentially when the script is run. Scripts allow users to automate repetitive tasks, perform complex computations, and organize code logic into reusable units. MATLAB scripts are particularly useful for prototyping algorithms, conducting analyses, and generating visualizations in a structured and reproducible manner.
Key Components of MATLAB Scripts: Before delving into creating and running MATLAB scripts, it’s essential to understand the key components and structure of a typical MATLAB script:
- Comments: Comments in MATLAB scripts begin with the percent symbol (%) and are used to provide explanations, documentation, or notes within the code. Comments are ignored by MATLAB during script execution.
- MATLAB Commands: MATLAB commands are statements that perform specific actions or operations, such as defining variables, performing calculations, calling functions, and generating plots.
- Variable Assignments: MATLAB scripts often involve assigning values to variables, which are placeholders for data or results used in computations and analyses.
- Control Flow Statements: Control flow statements, such as loops (for, while) and conditional statements (if, else), are used to control the flow of execution in MATLAB scripts based on certain conditions or criteria.
- Plotting Commands: MATLAB scripts often include commands for creating visualizations, such as plots, charts, and graphs, to illustrate data or results.
Creating a MATLAB Script: The process of creating a MATLAB script involves several steps, from opening a new script file to writing and saving the script with an appropriate filename. Here’s a comprehensive guide to creating a MATLAB script:
- Open MATLAB: Launch MATLAB on your computer or access it through an online platform, such as MATLAB Online or MATLAB Desktop Online.
- Open New Script: In the MATLAB Command Window or Editor window, go to the “File” menu and select “New Script” to open a new script file.
- Write MATLAB Commands: Write or copy-paste MATLAB commands and statements into the script file to perform desired computations, analyses, or tasks.
- Add Comments: Insert comments throughout the script to provide explanations, clarify code logic, or document the purpose of specific sections or commands.
- Save Script: Save the script file with an appropriate filename and the “.m” file extension, which indicates that it is a MATLAB script file. Choose a location on your computer where you can easily access and manage the script.
Running a MATLAB Script: Once a MATLAB script has been created and saved, it can be executed to run the commands and perform the desired actions or computations. Here’s how to run a MATLAB script:
- Navigate to Script: Locate the saved MATLAB script file in the MATLAB Current Folder or File Explorer.
- Open Script: Double-click on the script file to open it in the MATLAB Editor window.
- Run Script: In the MATLAB Editor window, click on the “Run” button (green triangle icon) or press the “F5” key to execute the entire script from start to finish.
- View Output: Monitor the MATLAB Command Window for any output, results, or errors generated during script execution. MATLAB will display messages, warnings, or errors encountered during script execution in the Command Window.
Best Practices for Creating and Running MATLAB Scripts: In addition to following the step-by-step guidelines outlined above, here are some best practices to optimize the creation and execution of MATLAB scripts:
- Use Descriptive Variable Names: Choose meaningful and descriptive names for variables to enhance code readability and maintainability.
- Break Code into Sections: Organize MATLAB scripts into sections using section delimiters (double percent symbols: %%), which can be collapsed or expanded for better code navigation.
- Test Incrementally: Test MATLAB scripts incrementally by running small sections or portions of the code to identify and debug errors or issues more effectively.
- Document Code: Document MATLAB scripts with comments to provide context, explain assumptions, and guide users through the code logic and functionality.
- Version Control: Use version control systems, such as Git or SVN, to track changes, manage revisions, and collaborate on MATLAB scripts with team members or collaborators.
Conclusion: Creating and running MATLAB scripts is a fundamental skill for users seeking to leverage the full power and versatility of MATLAB for data analysis, numerical computation, and algorithm development. By following the comprehensive guide and best practices outlined above, users can create structured, efficient, and reproducible MATLAB scripts to automate tasks, perform computations, and visualize data with ease. With its intuitive syntax, extensive documentation, and interactive development environment, MATLAB empowers users to transform their ideas into reality, explore complex problems, and innovate solutions across a wide range of domains and disciplines. Whether it’s prototyping algorithms, conducting simulations, or analyzing experimental data, MATLAB scripts provide a flexible and powerful framework for tackling real-world challenges and advancing scientific and engineering research and innovation.