In the fast-paced world of automotive innovation, Tesla has been a pioneer in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. At the forefront of this innovation is Tesla’s Autopilot system, a groundbreaking suite of advanced driver-assistance features. This extensive exploration delves into Autopilot 2.0, Tesla’s ambitious initiative aimed at achieving full autonomy, unraveling the technology, challenges, and the transformative impact it holds for the future of transportation.
- Evolution of Autopilot: From Conventional to Cutting-Edge
Tesla’s journey into autonomous driving began with the introduction of Autopilot in 2014. Initially a driver-assistance feature, Autopilot has evolved through continuous updates, incorporating advanced capabilities that bring the concept of self-driving cars closer to reality. Autopilot 2.0 represents a significant leap forward in this trajectory, introducing a comprehensive hardware and software overhaul.
- Hardware Suite: The Foundation for Full Autonomy
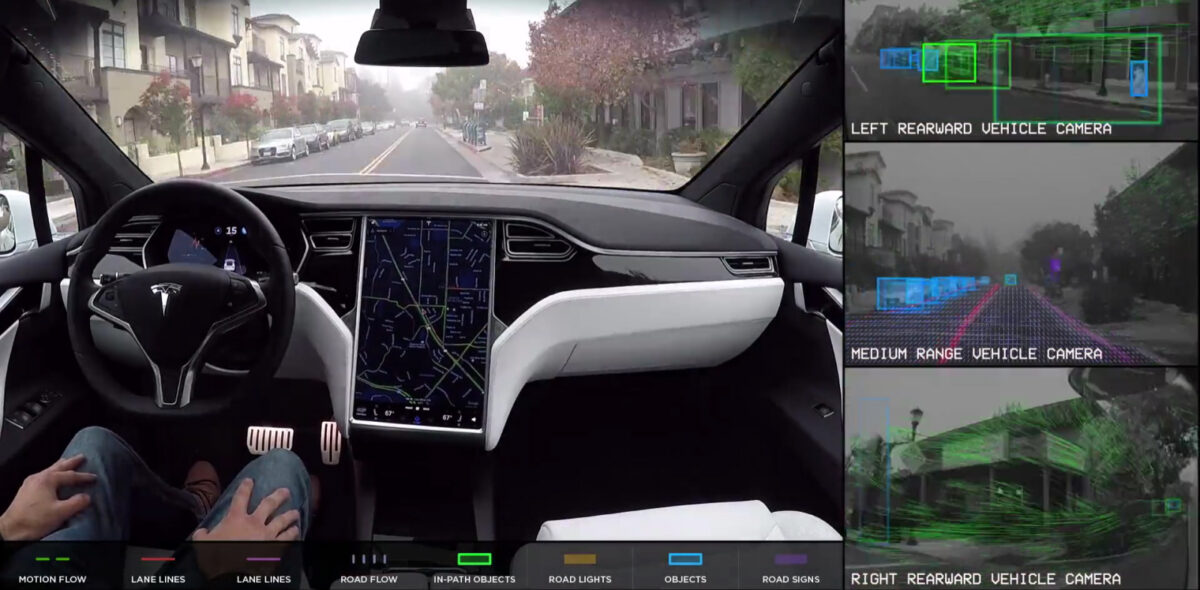
Autopilot 2.0 is built on a sophisticated hardware suite that serves as the eyes and ears of Tesla vehicles. The hardware includes an array of cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and radar, working in concert to provide a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings. The integration of this advanced sensor suite lays the foundation for Tesla’s vision of achieving full autonomy.
- Neural Networks and Machine Learning: Tesla’s Driving Brain
At the heart of Autopilot 2.0 is Tesla’s utilization of neural networks and machine learning algorithms. These technologies enable the vehicle to interpret and respond to complex driving scenarios by learning from vast amounts of real-world data. As Tesla vehicles gather more on-road experience, the neural networks evolve, improving the overall performance and safety of Autopilot.
- Autosteer and Navigate on Autopilot: A Dynamic Driving Duo
Autopilot 2.0 introduces features like Autosteer and Navigate on Autopilot, which enable the vehicle to autonomously navigate through traffic, change lanes, and follow a GPS route. These capabilities represent a substantial step towards automating highway driving, providing a glimpse into the future where drivers can relinquish control during specific driving scenarios.
- Full Self-Driving (FSD) Capability: The Vision for Full Autonomy
Tesla’s Autopilot 2.0 is part of the broader Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability, a vision that aims to enable fully autonomous driving. While FSD is not fully realized as of now, Tesla continually releases over-the-air updates that enhance Autopilot’s capabilities, bringing the company closer to achieving a level of autonomy where human intervention is minimal or unnecessary.
- Autopilot Safety Features: Mitigating Risks and Enhancing Security
Autopilot 2.0 is designed with safety as a top priority. The system includes features such as Automatic Emergency Braking, Collision Avoidance Assist, and Traffic-Aware Cruise Control, all working together to mitigate risks and enhance the overall security of Tesla vehicles. These safety features are integral to the gradual progression towards full autonomy.
- Challenges on the Road to Full Autonomy: Regulatory, Ethical, and Technical Hurdles
The road to achieving full autonomy is fraught with challenges. Regulatory frameworks, ethical considerations, and technical hurdles represent significant obstacles that must be navigated. As Tesla continues to advance its Autopilot technology, collaboration with regulatory bodies, adherence to ethical standards, and overcoming technical limitations are essential for realizing the vision of full autonomy.
- Autopilot in Real-World Scenarios: A User-Centric Perspective
Users’ experiences with Autopilot 2.0 provide valuable insights into the system’s capabilities and limitations. Real-world scenarios, from highway cruising to navigating complex city environments, contribute to the ongoing refinement of Tesla’s autonomous driving algorithms. User feedback serves as a crucial feedback loop, helping Tesla enhance the system’s performance and address edge cases.
- Tesla’s Approach to Autonomy: Iterative Development and Continuous Improvement
Tesla’s approach to achieving full autonomy is characterized by iterative development and continuous improvement. The company’s ability to deploy software updates over the air allows Tesla vehicles to evolve dynamically, benefiting from the collective experiences of the entire fleet. This approach positions Tesla at the forefront of the automotive industry’s shift towards software-centric development.
- The Future of Autopilot: Beyond the Horizon of Full Autonomy
The vision of full autonomy holds profound implications for the future of transportation. As Tesla refines Autopilot 2.0 and works towards realizing the complete self-driving capability, the automotive landscape is poised for a transformative shift. The future may see a paradigm where vehicles become interconnected nodes in a larger transportation network, optimizing traffic flow, reducing accidents, and reshaping the way we think about mobility.
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Landscape: Navigating Legal and Policy Frameworks
The deployment of fully autonomous vehicles raises complex legal and regulatory questions. Tesla, along with other industry players, must collaborate with governments and regulatory bodies to establish clear frameworks that ensure the safe and responsible deployment of autonomous driving technology.
- Ethical Considerations: Addressing Moral Dilemmas in Autonomous Driving
Autonomous vehicles must grapple with ethical considerations, such as decision-making in scenarios where a collision is inevitable. Tesla and the industry at large need to engage in transparent discussions about the ethical principles that should guide autonomous systems and ensure alignment with societal values.
- Public Perception and Trust: Building Confidence in Autonomous Technology
Achieving widespread acceptance of autonomous technology requires building public trust. Tesla’s transparency in communicating the capabilities and limitations of Autopilot, as well as demonstrating a commitment to safety, is crucial for instilling confidence in users and the general public.
- Cybersecurity: Safeguarding Autonomous Systems from Threats
As vehicles become increasingly reliant on software and connectivity, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Tesla must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to protect autonomous systems from potential threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of the vehicles and their occupants.
Conclusion
Tesla’s Autopilot 2.0 represents a monumental leap towards achieving full autonomy in the realm of automotive technology. From the integration of advanced hardware to the deployment of neural networks and machine learning algorithms, Tesla’s approach to autonomous driving is characterized by innovation, iterative development, and a commitment to safety. As the company navigates the road to full autonomy, challenges such as regulatory frameworks, ethical considerations, and technical hurdles must be addressed collaboratively with industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies. The transformative impact of full autonomy extends beyond individual vehicles, potentially reshaping the entire landscape of transportation and mobility. Tesla’s vision for Autopilot 2.0 and Full Self-Driving capability reflects not just a technological milestone but a paradigm shift that could redefine how we move and interact with vehicles in the future. Beyond the horizon of full autonomy, Tesla is steering towards a future where the driver’s seat may become optional, and the concept of driving is redefined by the marriage of cutting-edge technology and automotive ingenuity.