In the realm of computer-aided design (CAD), blocks serve as fundamental elements for creating, organizing, and reusing geometry and data within drawings. Mastering the techniques for creating and inserting blocks in AutoCAD is essential for enhancing productivity, maintaining consistency, and streamlining workflows in various design projects. Whether you’re an architect, engineer, designer, or drafting professional, understanding how to effectively create and insert blocks empowers you to efficiently manage complex geometry and data within your drawings. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the tools and techniques for creating and inserting blocks in AutoCAD, discuss their applications and functionalities, and provide step-by-step instructions to help you refine your drafting skills and unlock new possibilities in your design projects.
Understanding Blocks in AutoCAD:
Before delving into the specifics of creating and inserting blocks in AutoCAD, it’s essential to grasp the concepts and functionalities of blocks:
- Block Objects: In AutoCAD, a block is a collection of one or more objects that are combined into a single entity. Blocks can consist of geometric shapes, text, attributes, or even other blocks, and they enable users to efficiently manage and manipulate complex geometry within drawings.
- Block References: Block references, also known as block instances, are instances of a block inserted into a drawing. When you insert a block reference, you create a link to the original block definition, allowing you to reuse and modify the block across multiple instances within the drawing.
Creating Blocks in AutoCAD:
AutoCAD provides a variety of tools and commands for creating blocks, allowing users to define reusable elements that can be inserted into drawings as needed. Here’s how to create blocks in AutoCAD:
- Defining Block Geometry:
- Select the objects you want to include in the block and ensure they are positioned and oriented as desired within the drawing.
- Type “BLOCK” in the command line or click on the Block Definition tool in the Insert panel on the Home tab of the Ribbon to open the Block Definition dialog box.
- Specifying Block Properties:
- In the Block Definition dialog box, specify a name for the block and a base point that defines the insertion point when you insert the block into a drawing.
- Optionally, specify additional settings such as scale, rotation, and visibility for the block.
- Creating the Block:
- Click “OK” to create the block definition. AutoCAD prompts you to select the objects you want to include in the block.
- Select the objects and press “Enter” to confirm your selection. AutoCAD creates the block definition and prompts you to insert the block into the drawing.
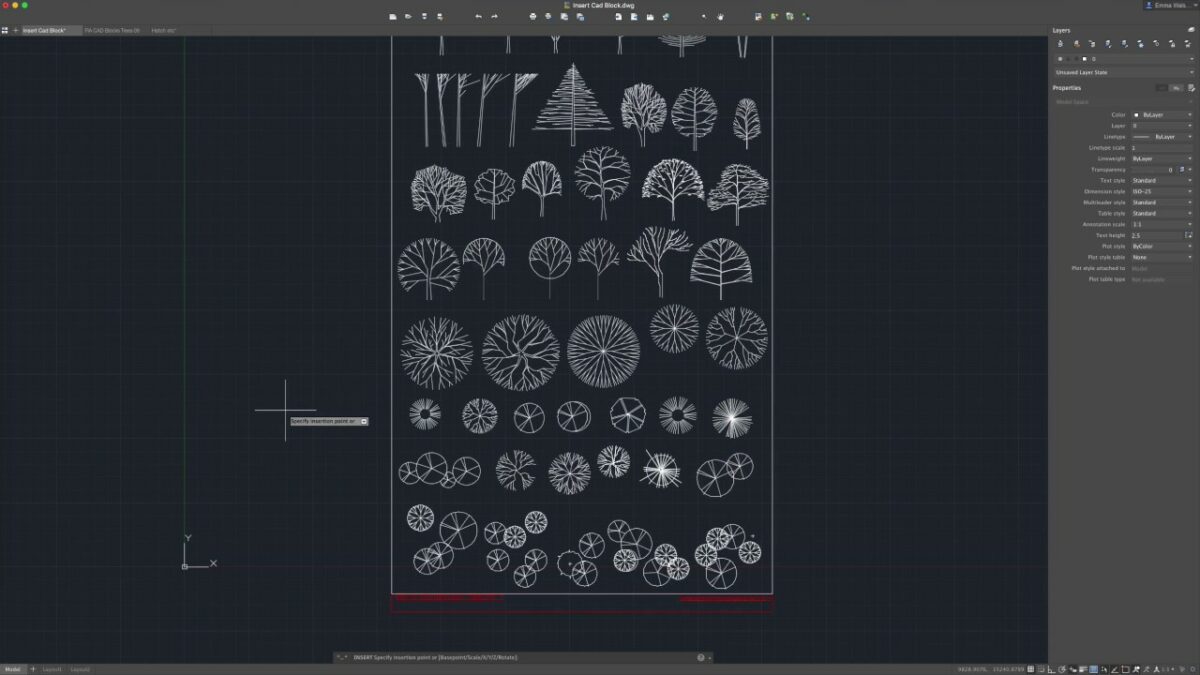
Inserting Blocks in AutoCAD:
Once you’ve created block definitions, you can insert them into your drawing as block references. Here’s how to insert blocks in AutoCAD:
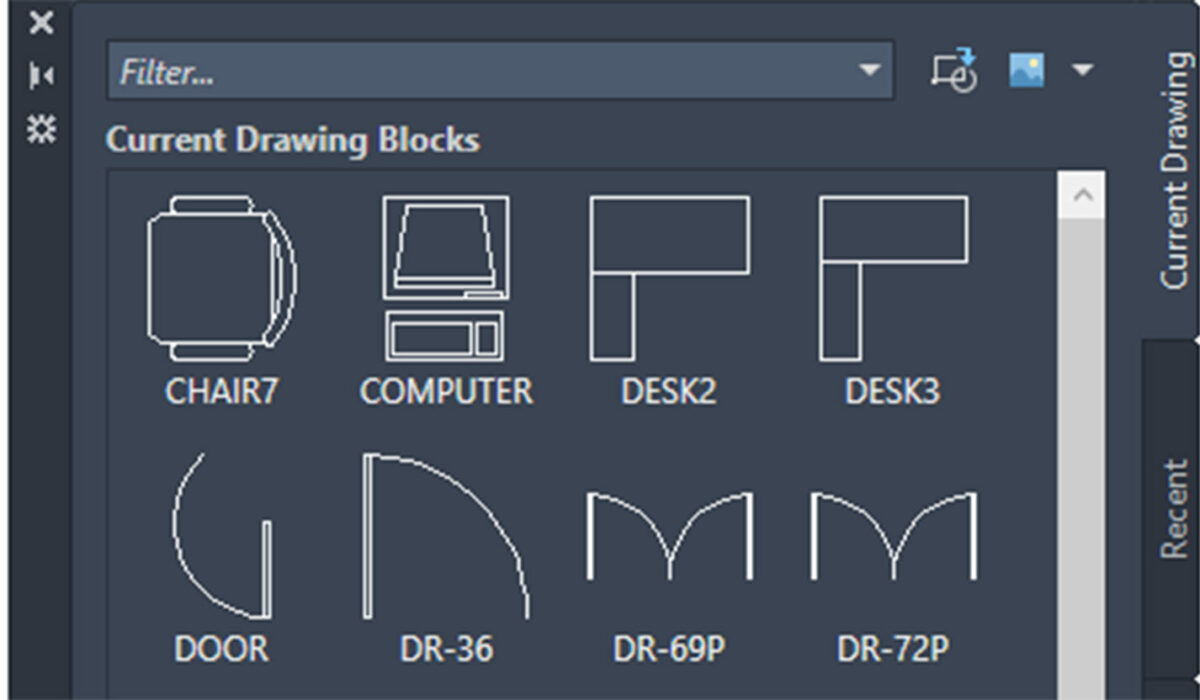
- Using the Insert Command:
- Type “INSERT” in the command line or click on the Insert tool in the Blocks panel on the Home tab of the Ribbon.
- In the Insert dialog box, select the block you want to insert from the block library or browse for the block file on your computer.
- Specifying Insertion Options:
- Specify the insertion point for the block by clicking in the drawing area or entering precise coordinates. You can also specify additional insertion options such as scale, rotation, and mirroring.
- Placing the Block:
- Click to place the block in the drawing. AutoCAD inserts the block reference at the specified insertion point, creating a link to the original block definition.
Advanced Techniques for Creating and Inserting Blocks:
In addition to basic block creation and insertion tools, AutoCAD offers advanced techniques for optimizing block usage and enhancing productivity:
- Dynamic Blocks: Create dynamic blocks in AutoCAD to add intelligence and interactivity to block instances. Dynamic blocks allow users to modify block geometry, visibility, and properties using grips and parameters, enabling greater flexibility and customization.
- External References (Xrefs): Use external references (Xrefs) to reference and incorporate blocks from external drawing files into your current drawing. Xrefs facilitate collaboration, version control, and modular design workflows by allowing multiple users to work on different parts of a design simultaneously.
- Block Libraries: Build and maintain block libraries containing commonly used blocks, symbols, and components to streamline design workflows and ensure consistency across projects. Organize block libraries by category, type, or project to facilitate easy access and reuse.
- Nested Blocks: Create nested blocks by inserting one block into another block, allowing you to build complex assemblies and hierarchical structures within drawings. Nested blocks provide a modular approach to design and enable efficient management of intricate geometry.
Best Practices for Creating and Inserting Blocks:
To maximize efficiency and maintain consistency when creating and inserting blocks in AutoCAD, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Standardize Block Naming: Establish and adhere to a consistent naming convention for blocks to ensure clarity and organization within block libraries and drawings.
- Document Block Properties: Document block properties, attributes, and usage guidelines to facilitate collaboration and ensure accurate interpretation of block content by other users.
- Reuse Existing Blocks: Prioritize the reuse of existing blocks whenever possible to minimize redundancy, maintain consistency, and optimize drawing file size.
- Review and Update Blocks: Regularly review and update block definitions to incorporate design changes, corrections, or improvements and ensure that all block instances reflect the latest revisions.
Conclusion:
Mastering the techniques for creating and inserting blocks in AutoCAD is essential for enhancing productivity, maintaining consistency, and streamlining workflows in various design projects. By understanding the functionalities of blocks, practicing their use in different design scenarios, and implementing best practices for efficiency and consistency, you can elevate your drafting skills and unlock new possibilities in your design projects. Whether you’re creating architectural plans, mechanical drawings, or electrical schematics, knowing how to create and insert blocks effectively will enable you to produce high-quality drawings with confidence and precision. With dedication, practice, and a commitment to continuous learning, you’ll become proficient in working with blocks in AutoCAD and excel in your CAD design endeavors.