Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), AutoCAD stands as a cornerstone, empowering designers and engineers to bring their ideas to life. Beyond the traditional drafting functionalities, AutoCAD offers a powerful feature that enhances the intelligence and information embedded within drawings – the ability to add data attributes to objects. This extensive guide delves into the intricacies of this feature, exploring how data attributes can elevate your AutoCAD drawings by providing valuable information, improving collaboration, and streamlining data management.
Section 1: Understanding Data Attributes in AutoCAD
1.1 Introduction to Data Attributes: Data attributes, also known as object data or custom properties, allow users to attach additional information to AutoCAD objects. Explore how these attributes go beyond geometric properties, enabling users to include data such as material, cost, manufacturer, and more, turning drawings into comprehensive databases.
1.2 Importance of Data Attributes: Delve into the significance of incorporating data attributes in AutoCAD drawings. Understand how this feature enhances the intelligence of designs, streamlines documentation, and facilitates better decision-making throughout the design, construction, and maintenance phases of a project.
Section 2: Types of Objects with Data Attributes
2.1 Adding Data to Basic Objects: Learn how to add data attributes to fundamental AutoCAD objects. From lines and circles to rectangles and polygons, explore the process of attaching custom information to these objects, making them more informative and contextually rich.
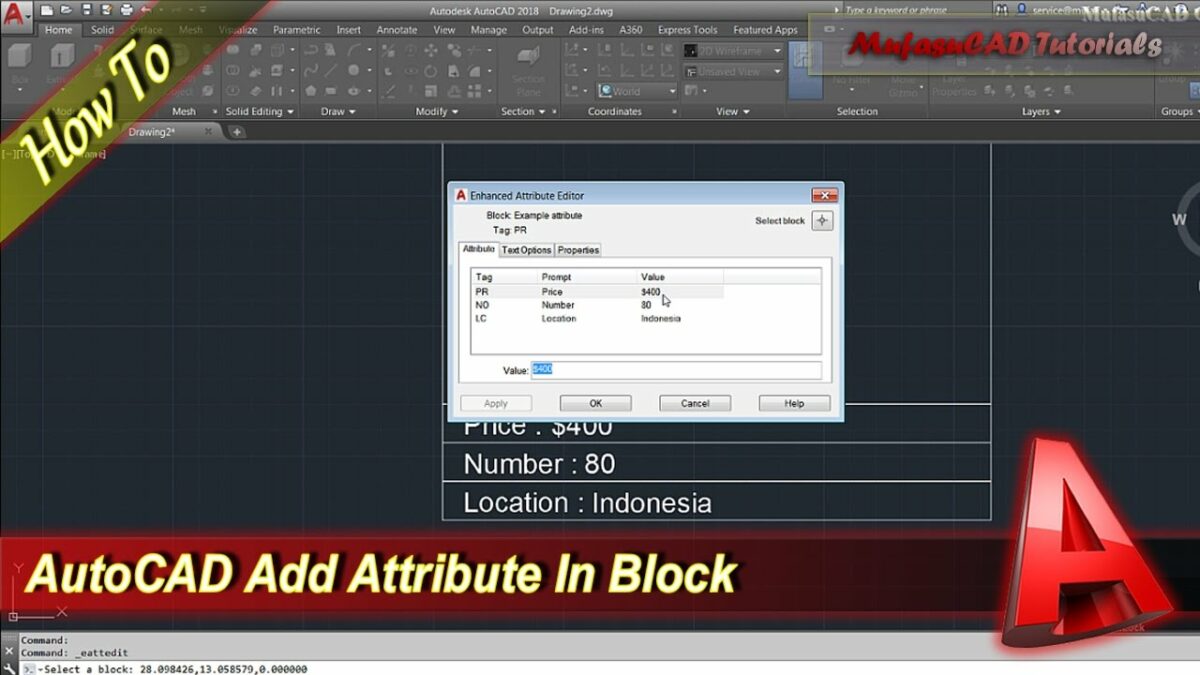
2.2 Data Attributes for Blocks: Discover the power of associating data attributes with blocks in AutoCAD. Understand how this functionality extends to dynamic blocks, allowing for the inclusion of parameters and attributes that can be manipulated to meet specific design criteria.
2.3 Attaching Data to Text and Dimensions: Explore the incorporation of data attributes within text and dimension entities. Learn how to add information such as specifications, notes, or cost details, providing a comprehensive understanding of the design intent.
Section 3: Setting Up Data Attributes in AutoCAD
3.1 Accessing the Properties Palette: Master the use of the Properties palette in AutoCAD to access and modify data attributes. Understand how this centralized interface allows users to view and edit various properties associated with selected objects efficiently.
3.2 Defining Custom Properties: Learn the process of defining custom properties for AutoCAD objects. Explore the creation of user-specific data fields that align with project requirements, ensuring that the added attributes are tailored to capture relevant information.
Section 4: Associating External Data with AutoCAD Objects
4.1 Linking External Databases: Delve into the integration of external databases with AutoCAD objects. Explore how to establish a link between your drawing and external data sources, enabling real-time updates and synchronization of information.
4.2 Excel Integration: Learn how to seamlessly integrate Excel spreadsheets with AutoCAD objects. Understand the process of linking cells in Excel to data attributes in AutoCAD, facilitating dynamic data management and collaboration between design and spreadsheet applications.
Section 5: Extracting and Reporting Data Attributes
5.1 Using the Data Extraction Wizard: Master the Data Extraction Wizard in AutoCAD. Explore how this tool enables users to extract specific data attributes from multiple objects, creating customized tables and reports that streamline data analysis and project documentation.
5.2 Generating Tables and Reports: Learn how to generate tables and reports based on extracted data attributes. Explore the flexibility of AutoCAD in presenting data in tabular formats, making it accessible for project stakeholders and aiding in decision-making processes.
Section 6: Advanced Techniques for Data Attributes
6.1 Dynamic Data Linking: Delve into dynamic data linking in AutoCAD. Explore how to establish a dynamic connection between attributes and external data sources, ensuring that changes in the source data reflect instantly in the drawing, promoting accuracy and consistency.
6.2 Implementing Data Validation: Understand the importance of data validation in AutoCAD. Explore techniques to implement validation rules, ensuring that the entered data adheres to predefined criteria, minimizing errors and enhancing the reliability of the information.
Section 7: Collaborative Workflows with Data Attributes
7.1 Sharing Drawings with Data Attributes: Explore best practices for sharing AutoCAD drawings with embedded data attributes. Understand how to ensure data consistency when collaborating with team members or stakeholders, regardless of their access to external databases.
7.2 Collaborating with Autodesk A360: Discover the collaborative potential of Autodesk A360 in managing drawings with data attributes. Learn how cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless collaboration, allowing multiple users to access and contribute to the design documentation.
Section 8: Challenges and Troubleshooting
8.1 Common Challenges in Managing Data Attributes: Address common challenges encountered in managing data attributes in AutoCAD. From issues with data consistency to challenges in linking external databases, gain insights into effective problem-solving strategies for maintaining data integrity.
8.2 Troubleshooting Tips: Explore troubleshooting tips for resolving issues related to data attributes in AutoCAD. From ensuring proper data linking to addressing conflicts in attribute definitions, understand how to maintain precision and stability in your design process.
Section 9: Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
9.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: Delve into the potential integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in managing data attributes in AutoCAD. Explore how AI algorithms may assist in automating data entry, validation, and analysis, enhancing efficiency in design workflows.
9.2 Augmented Reality (AR) for Data Visualization: Explore the integration of augmented reality (AR) with data attributes in AutoCAD. Learn how AR technologies enhance the immersive experience of interacting with and visualizing data-rich designs in real-world contexts.
Conclusion:
As we conclude this exhaustive exploration of adding data attributes to AutoCAD objects, it is evident that the power of information extends beyond geometric entities. By leveraging data attributes, designers and engineers can create intelligent drawings that serve as comprehensive repositories of information. AutoCAD’s robust capabilities in managing data attributes empower users to enhance collaboration, streamline documentation, and make informed decisions throughout the lifecycle of a project. Embrace the versatility, efficiency, and customization that AutoCAD offers in managing data attributes, and witness how this transformative skill elevates your designs from mere drawings to dynamic, information-rich assets. With continuous practice, exploration, and innovation, you will navigate the intricate landscape of data attributes in AutoCAD with confidence, producing drawings that stand as testaments to the power of CAD in the dynamic world of design and engineering.