Using layers effectively in BricsCAD is essential for organizing and managing drawing elements, enhancing workflow efficiency, and maintaining clarity in CAD projects. Layers provide a structured way to control the visibility, editing, and properties of different components within a drawing. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the detailed process of using layers in BricsCAD, covering fundamental concepts, layer management techniques, best practices, and practical applications.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Layers in BricsCAD
- Understanding Layer Basics
- Creating and Managing Layers
- Assigning Properties to Layers
- Layer States and Filters
- Working with Layer Tools
- Layer Management Best Practices
- Layer Applications in Different Industries
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Layers in BricsCAD
Layers in BricsCAD serve as organizational tools that allow users to group and manage drawing entities based on different properties and characteristics. By assigning entities to specific layers, users can control visibility, plotting, and editing properties, thereby enhancing the clarity and efficiency of CAD drawings.
2. Understanding Layer Basics
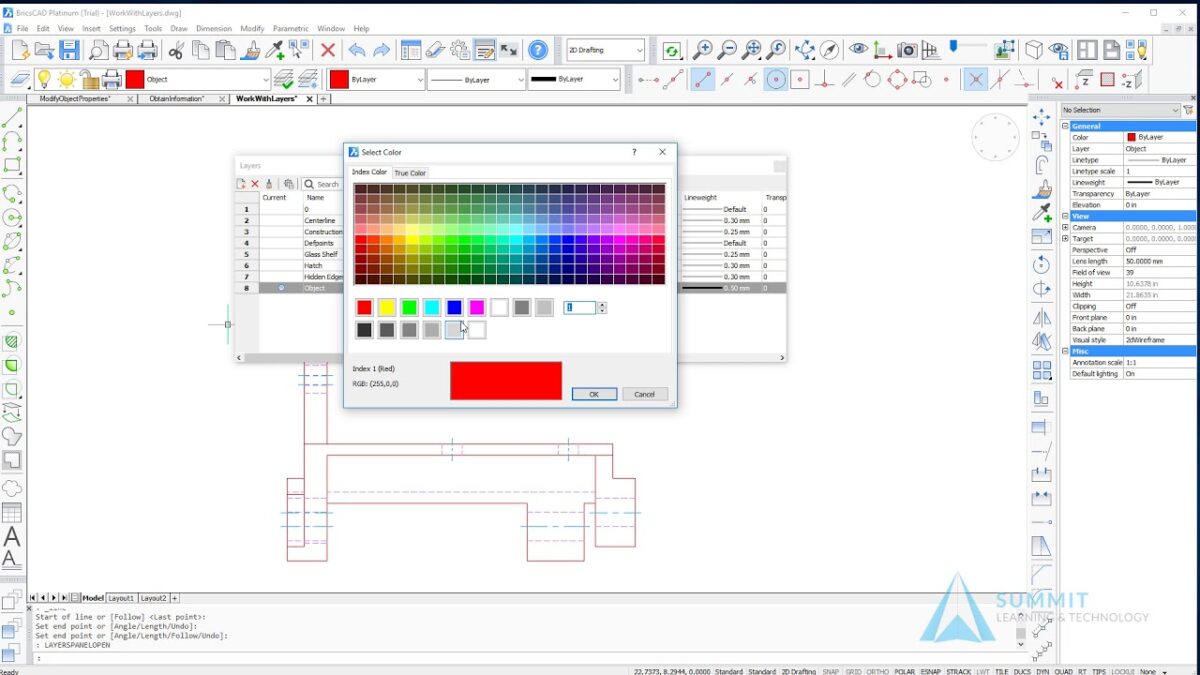
- Layer Properties: Each layer in BricsCAD can have unique properties such as color, line type, line weight, transparency, and plot style.
- Layer Visibility: Layers can be turned on or off to control the display of associated entities within the drawing viewport.
- Layer Order: Layers can be arranged in a stacking order to determine the visibility priority of overlapping entities.
3. Creating and Managing Layers
- Creating New Layers: Use the
LAYERcommand to create new layers or import layer definitions from existing drawings. - Renaming and Deleting Layers: Rename layers to reflect their purpose or delete unused layers to streamline the drawing.
4. Assigning Properties to Layers
- Layer Properties Manager: Access the Layer Properties Manager to view and modify layer properties.
- Assigning Properties: Set properties such as color, line type, and line weight for each layer to differentiate drawing elements.
5. Layer States and Filters
- Layer States: Save and restore different combinations of layer settings (e.g., visibility, properties) using layer states.
- Layer Filters: Use layer filters to selectively display or isolate specific layers based on criteria such as name, color, or property.
6. Working with Layer Tools
- Layer Freeze and Thaw: Temporarily hide or display layers without affecting their properties using freeze and thaw commands.
- Layer Lock and Unlock: Prevent or allow editing of entities on locked layers to maintain drawing integrity.
7. Layer Management Best Practices
- Consistent Naming Convention: Adopt a standardized naming convention for layers to facilitate easy identification and organization.
- Use of Layer Groups: Group related layers into sets or categories to streamline management and improve workflow efficiency.
8. Layer Applications in Different Industries
Layers play a crucial role across various industries and applications:
- Architecture: Organize floor plans, elevations, and construction details on separate layers.
- Mechanical Engineering: Manage assembly components, dimensions, and annotations using dedicated layers.
- Electrical Design: Separate wiring diagrams, symbols, and annotations into distinct layers for clarity and efficiency.
9. Conclusion
Mastering the use of layers in BricsCAD enhances productivity, improves drawing organization, and facilitates effective collaboration in CAD projects. By leveraging layer management tools and best practices, users can streamline workflows, maintain drawing clarity, and optimize design processes across different disciplines and industries. Whether you’re creating architectural plans, mechanical drawings, or electrical schematics, understanding and implementing layers effectively in BricsCAD ensures that your CAD projects are well-structured, easily navigable, and meet professional standards. Continuous practice, exploration of advanced layer functionalities, and adherence to industry-specific requirements contribute to achieving superior outcomes in CAD design and drafting with BricsCAD.